How to Verify If a Claim Is True: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Verifying Claims
In the digital age, information flows rapidly, making it easy to come across various claims that may or may not be true. Whether it’s a social media post, a news article, or even a personal anecdote, verifying the accuracy of a claim is critical. This article provides a comprehensive guide to assessing the truthfulness of claims using reliable methods.
Learning how to verify a claim is a valuable skill in today’s world of instant information sharing. From checking credible sources to understanding fact-checking techniques, this guide will help you become proficient in validating claims effectively.
1. How Can I Evaluate the Credibility of a Source?
To verify if a claim is true, start by evaluating the credibility of the source. Knowing how to assess sources is crucial because credible sources are more likely to report accurate information. Below are steps you can use to evaluate a source’s credibility:
- Check the author’s credentials: Does the author have relevant expertise or professional background in the topic?
- Look for reputable affiliations: Publications or platforms with reputable affiliations often provide more accurate information.
- Assess the site’s domain: Domains like “.edu” or “.gov” are generally more trustworthy than personal blogs or lesser-known websites.
- Evaluate the tone: Reliable sources present information in a neutral, unbiased manner.
- Confirm if the source includes citations: References to research or other trusted sources indicate thorough reporting.

2. What Are Reliable Fact-Checking Methods?
Using fact-checking techniques is essential when determining if a claim is accurate. These methods are structured and provide objective ways to verify statements.
- Cross-reference information: Look for the same claim on multiple trustworthy websites.
- Utilize fact-checking sites: Websites like Snopes, FactCheck.org, and PolitiFact are dedicated to verifying news and rumors.
- Check for primary sources: Whenever possible, refer to primary sources instead of relying on second-hand information.
3. How Do I Identify Potential Bias in a Claim?
Bias can affect how information is presented, so recognizing it is a critical part of verifying claims. Use the following indicators to identify bias:
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Language | Examine if the language is emotional or opinionated. |
| Selective Reporting | Check if the source selectively reports information that supports a particular view. |
| Source History | Research the source’s history for patterns of biased reporting. |

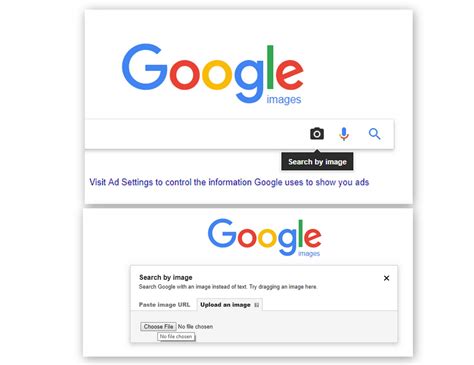
4. How Can I Use Reverse Image Search for Verification?
Reverse image search is a practical tool for verifying the authenticity of images associated with claims. Using tools like Google Images or TinEye, follow these steps:
- Save or copy the image from the source.
- Go to a reverse image search engine, such as Google Images.
- Upload or paste the image URL to see where else it appears online.
5. How Can I Verify News from Social Media?
Social media platforms are known for spreading information quickly, which makes verifying news from these sources essential. Here are some effective methods:
- Look for verification badges: Verified profiles (often with a blue checkmark) are more trustworthy.
- Search for the same news on reliable news websites: Cross-check if reputable news sources are reporting the same story.
- Beware of altered images or videos: Editing tools can manipulate content to mislead viewers.
6. What Role Do Primary Sources Play in Verification?
Primary sources are original documents or firsthand accounts. These are crucial for verifying claims because they provide the closest version to the truth.
- Directly consult the primary source: This could be an official report, speech, or an eyewitness account.
- Verify quotes and data: Ensure that data or quotes are not taken out of context by comparing with the primary source.
- Assess if the primary source is accessible: Reputable sources often make primary sources accessible for verification.
7. How to Spot Misinformation and Fake News?
Detecting fake news requires attention to detail. Key indicators include:
- Sensationalism: Misinformation often uses exaggerated headlines.
- Lack of reputable sources: Claims that lack references to established sources may be fabricated.
- Examine the publication date: Old news can be re-shared to create false impressions.
8. How to Recognize Expert Opinion and Fact?
Sometimes claims may come from experts, but not all expert opinions are facts. To differentiate, consider:
- Check the expert’s credentials: Ensure the expert has a verified background relevant to the claim.
- Understand if it’s a fact or prediction: Predictions are often educated guesses, not facts.
- Look for consensus: When multiple experts agree, the claim is more likely to be credible.
9. How Do I Verify Scientific Claims?
Scientific claims require a specific verification process. Here are steps to follow:
- Identify the research journal: Reputable journals are more likely to publish valid studies.
- Check if the study is peer-reviewed: Peer-reviewed studies have been examined by other experts in the field.
- Examine sample size and methodology: Reliable studies usually have a sufficient sample size and rigorous methodology.
10. How Do I Distinguish Between Correlation and Causation?
It’s essential to understand the difference between correlation and causation when verifying claims. Not all correlations imply causation, so follow these guidelines:
- Look for additional supporting evidence: Causal claims require multiple supporting studies.
- Consider alternative explanations: A correlation might be due to a third factor, not direct causation.
- Use caution with assumptions: Avoid assuming causation unless the claim clearly explains the link.
Summary Table
| Verification Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Credibility | Evaluating the reputation and background of the information source. |
| Fact-Checking Sites | Using reputable sites like Snopes for cross-referencing claims. |
| Primary Sources | Directly accessing firsthand sources for reliable information. |
FAQ
What are some reliable fact-checking websites?
Some trustworthy sites include Snopes, FactCheck.org, and PolitiFact.
How do I verify a claim without any sources?
If sources are unavailable, look for similar claims on reputable websites or consult experts in the field.
What are the signs of misinformation?
Misinformation often includes sensational language, lack of credible sources, and out-of-context details.
Is reverse image search effective?
Yes, reverse image search can help identify the origin of an image, revealing if it’s been used elsewhere.
What role does primary research play?
Primary research offers the closest version of truth, directly from the original source.
How can I tell if an expert opinion is credible?
Check the expert’s background, field relevance, and consensus with other experts.
What’s the difference between correlation and causation?
Correlation is a relationship, while causation shows direct cause-and-effect. They are often mistaken.



