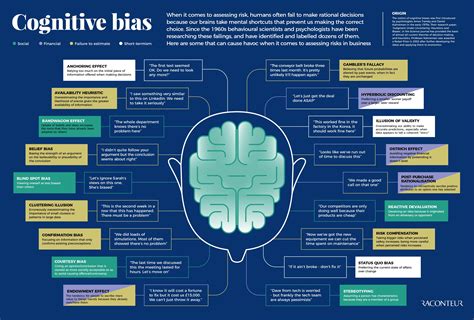
How Do Cognitive Biases Affect Perception?
1. What Are Cognitive Biases and How Do They Shape Our Perception?
Cognitive biases are systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment. They impact our perception and decision-making processes by causing us to interpret information through subjective lenses rather than objective analysis.
Cognitive biases influence how we see, understand, and interact with the world. They can lead us to form opinions based on incomplete information or personal beliefs rather than on facts. As a result, they can play a critical role in shaping our worldview and responses.
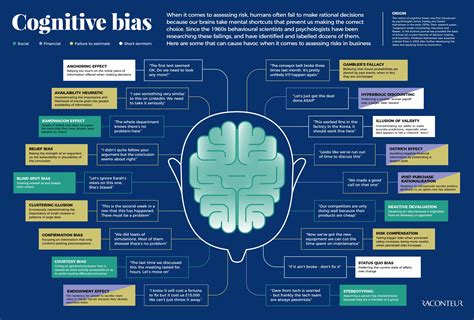
Some common cognitive biases that affect perception include:
- Confirmation Bias: Seeking out information that supports existing beliefs.
- Anchoring Bias: Relying heavily on the first piece of information encountered.
- Availability Heuristic: Overestimating the importance of information readily available.
- Overconfidence Bias: Having excessive confidence in one’s own knowledge or abilities.
These biases influence perception by creating shortcuts, or heuristics, that simplify information processing but often result in skewed or inaccurate interpretations.
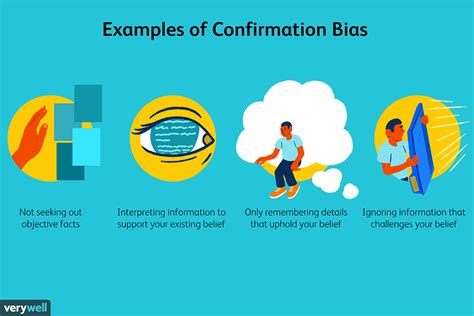
2. How Does Confirmation Bias Alter Our Understanding of Information?
Confirmation bias leads people to favor information that aligns with their beliefs while disregarding contradictory evidence. This bias affects perception by limiting our openness to new or opposing viewpoints.
Confirmation bias is especially influential in contexts like politics, social issues, and personal relationships. For example:
- A person with strong political views may only watch news sources that reflect their beliefs, reinforcing their perspectives.
- In personal relationships, people may interpret a partner’s actions in line with existing expectations, even if those interpretations are inaccurate.
| Situation | Confirmation Bias Effect |
|---|---|
| Researching Health Topics | Favoring articles that support pre-existing health beliefs. |
| Shopping Decisions | Focusing on positive reviews that confirm purchase decisions. |
In summary, confirmation bias shapes perception by reinforcing existing beliefs, often at the expense of objective analysis or balanced viewpoints.
3. Why Is Anchoring Bias Important in Decision-Making?
Anchoring bias is the tendency to rely heavily on the first piece of information, or anchor, when making decisions. This bias often skews perception by creating an undue emphasis on initial data or impressions.
In practical settings, anchoring can be seen in negotiation scenarios where the first proposed price tends to dominate the discussion. For example:
- In a salary negotiation, an initial offer might set a benchmark, making it difficult for either party to move significantly away from that number.
- In purchasing, the first price seen for a product may become the standard against which other prices are judged.
Anchoring bias affects perception and decision-making by narrowing our focus, sometimes leading to suboptimal choices based on limited initial information.
4. How Does Availability Heuristic Distort Our View of Reality?
The availability heuristic is a cognitive shortcut that relies on immediate examples that come to mind. It skews perception by causing people to overestimate the likelihood of events based on readily available information.
This bias is commonly seen in areas like:
- Media Influence: Frequent media coverage of specific events, like natural disasters, can lead people to believe these events are more common than they are.
- Personal Experiences: If someone has a recent experience with a particular issue, they may assume it’s widespread.

The availability heuristic can distort perception, creating fears or expectations that may not align with statistical reality.
5. How Does Overconfidence Bias Affect Our Perception of Competence?
Overconfidence bias occurs when individuals overestimate their abilities or knowledge. This bias can lead to poor decisions based on the mistaken belief in one’s capabilities.
Examples of overconfidence bias in daily life include:
- Driving: People often believe they are better-than-average drivers, leading to riskier behavior.
- Financial Decisions: Investors may overestimate their ability to predict market trends, resulting in risky choices.
| Scenario | Overconfidence Impact |
|---|---|
| Work Performance | May lead to overlooking areas needing improvement. |
| Health | Overestimating fitness level can result in injury. |
Overconfidence bias affects perception by creating an inflated sense of control or competence, which can lead to overreaching or inadequate preparation.
6. What Is the Halo Effect and How Does It Affect Judgments?
The halo effect is the tendency to let an initial positive impression of someone influence our perception of their other qualities. This cognitive bias often causes us to overlook flaws or make assumptions based on a single characteristic.
For example:
- A person who is physically attractive may also be perceived as more competent or friendly, regardless of their actual skills or personality.
- In job interviews, candidates with positive first impressions often receive favorable evaluations overall.
The halo effect shapes perception by leading us to extend positive attributes from one area to others, often without evidence.
7. How Does Stereotyping Affect Our Perception of Others?
Stereotyping is a cognitive bias that leads people to make generalized assumptions about individuals based on their membership in a particular group. This bias significantly impacts perception by shaping expectations and judgments based on group characteristics rather than individual attributes.
Stereotyping influences perceptions in various ways:
- Social Interactions: People may approach others differently based on stereotypes, affecting relationships.
- Hiring Decisions: Employers might make assumptions about a candidate based on stereotypical beliefs.
While stereotypes can simplify information processing, they often lead to biased and inaccurate perceptions.
8. What Is the Role of the Recency Effect in Shaping Perception?
The recency effect is a cognitive bias that causes people to recall the most recent information more vividly than older data. This tendency affects perception by emphasizing recent experiences over long-term information.
Examples of the recency effect include:
- Evaluating Employee Performance: Managers may give more weight to recent accomplishments.
- Consumer Reviews: Shoppers may focus on the latest reviews when deciding on a purchase.
The recency effect shapes perception by influencing what we remember and prioritize, often at the expense of earlier information.
9. How Does the Self-Serving Bias Affect Personal Perception?
Self-serving bias is the tendency to attribute positive outcomes to personal factors while blaming external factors for negative outcomes. This bias influences self-perception by protecting self-esteem but can hinder personal growth.
Examples include:
- A student attributing good grades to intelligence and poor grades to difficult exams.
- An athlete crediting wins to skill and losses to unfavorable conditions.
While the self-serving bias can boost self-confidence, it may prevent accurate self-assessment and improvement.
10. How Do Cultural Biases Shape Our Worldview?
Cultural biases arise from the influence of one’s culture on perception. These biases affect how people interpret information, often shaping their worldview in subtle ways.
Examples of cultural biases include:
- In business settings, attitudes toward hierarchy can differ, impacting workplace dynamics.
- Personal values, such as individualism or collectivism, influence behavior and expectations.
Cultural biases play a significant role in perception, often leading to misunderstandings across cultural divides.
Summary Table of Key Cognitive Biases and Their Effects
| Cognitive Bias | Description | Effect on Perception |
|---|---|---|
| Confirmation Bias | Favoring information that confirms beliefs | Narrowed perspective |
| Anchoring Bias | Relying on initial information | Limits further evaluation |
| Availability Heuristic | Relying on readily available examples | Distorted reality perception |
| Overconfidence Bias | Overestimating one’s abilities | Riskier decisions |
| Halo Effect | Assuming positive traits based on first impression | Skewed judgment |
FAQ
1. What is cognitive bias?
Cognitive bias is a pattern of deviation in judgment where individuals draw conclusions based on subjective preferences rather than objective reasoning.
2. How does confirmation bias affect relationships?
Confirmation bias in relationships can lead people to see partners’ actions through a biased lens, reinforcing existing beliefs and sometimes causing misunderstandings.
3. What is the difference between availability heuristic and confirmation bias?
The availability heuristic is based on accessible examples, while confirmation bias is the tendency to seek out information that confirms existing beliefs.
4. Can cognitive biases be minimized?
Yes, cognitive biases can be minimized through awareness, critical thinking, and decision-making practices that emphasize objectivity.
5. How does overconfidence affect decision-making?
Overconfidence can lead to risky decisions as people may overestimate their abilities or ignore potential risks.
6. What role does culture play in cognitive bias?
Culture influences cognitive biases by shaping values, expectations, and interpretations, which can affect interpersonal understanding and worldview.
7. How can organizations address cognitive biases?
Organizations can address cognitive biases by promoting awareness, diversity, and decision-making processes that challenge assumptions.