How Consumer Protection Acts Help Against Fakes
1. What are Consumer Protection Acts?
Consumer Protection Acts are laws designed to protect consumers from unfair trade practices and ensure their rights. These acts aim to create a safe marketplace by regulating the sale of goods and services. They provide consumers with mechanisms to seek redress for grievances related to faulty or counterfeit products.
One of the primary goals of these acts is to establish standards for product quality and safety. This helps in minimizing the risk of consumers purchasing fake or substandard products. The acts also set clear guidelines for businesses, ensuring they are held accountable for the products they sell.
Moreover, these acts empower consumers with rights that include the right to information, the right to choose, and the right to be heard. Such provisions encourage consumers to report fraudulent activities, thus enhancing market integrity.
In many jurisdictions, consumer protection agencies are established to enforce these laws. They investigate complaints and can take legal action against companies that violate consumer rights, thereby deterring the sale of counterfeit products.
Through these measures, Consumer Protection Acts play a crucial role in fostering trust between consumers and businesses, ultimately contributing to a healthier economy.
For instance, in the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is responsible for enforcing laws that prohibit deceptive business practices, including the sale of counterfeit goods.
Furthermore, the acts often include provisions for education and awareness, helping consumers to identify potential fakes. By informing consumers about their rights and the characteristics of genuine products, these acts work proactively against counterfeiting.
Lastly, international cooperation is often encouraged through these acts, allowing countries to work together in combating global counterfeit trade.

2. How do these acts prevent counterfeit products?
Consumer Protection Acts prevent counterfeit products through a variety of mechanisms designed to regulate the marketplace. These include stringent regulations on advertising and marketing practices, which are crucial in ensuring that consumers are not misled.
One key strategy is the requirement for businesses to provide clear and accurate information about their products. This transparency helps consumers make informed decisions and reduces the likelihood of purchasing counterfeit goods.
In addition, the acts often empower regulatory bodies to conduct inspections and audits of businesses. Regular checks help identify and eliminate sellers of counterfeit products, thereby enhancing consumer safety.
Legal penalties for violations of these acts serve as a strong deterrent against counterfeiting. Businesses caught selling fakes can face hefty fines and even criminal charges, making it risky to engage in such practices.
Another essential aspect is consumer education. Many consumer protection agencies run campaigns to inform the public about how to identify authentic products. By equipping consumers with knowledge, these acts effectively reduce the demand for counterfeit goods.

Consumer reporting mechanisms allow individuals to report suspicious products or practices directly to regulatory bodies. This grassroots involvement is vital for identifying and tackling counterfeiting at its roots.
Furthermore, the acts often facilitate collaboration between businesses and law enforcement agencies. Joint initiatives help to share information and resources in the fight against counterfeiting.
As a result, these comprehensive strategies significantly bolster consumer protection against fakes, fostering a safer marketplace for all.
3. What rights do consumers have under these acts?
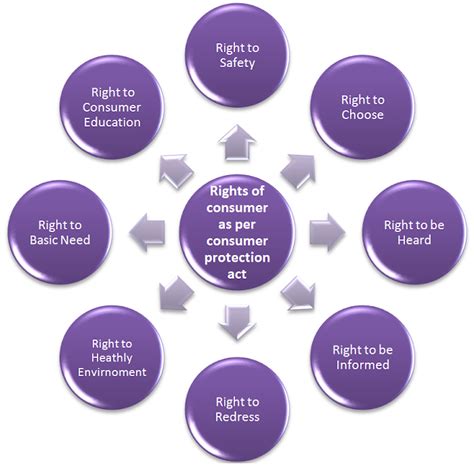
Consumers are endowed with several rights under Consumer Protection Acts, which are crucial in safeguarding them from fraudulent activities. The right to information is one of the most fundamental rights, ensuring that consumers are provided with complete details about products, including their origin, ingredients, and quality standards.
Additionally, consumers have the right to choose from a variety of products, free from any coercion or misleading information. This right is essential in promoting competition and driving innovation in the marketplace.
The right to safety is another critical aspect, ensuring that products are safe for consumption and do not pose any health risks. This right mandates businesses to comply with safety standards, thus reducing the chances of counterfeit or harmful products entering the market.
Moreover, consumers have the right to be heard. This includes the ability to voice complaints and seek redress when their rights are violated. Many consumer protection agencies have established channels for consumers to lodge grievances, ensuring that their concerns are addressed.
Under these acts, consumers are also entitled to fair treatment and freedom from unfair practices. This includes protection against deceptive advertising and fraudulent sales tactics.
Finally, the right to education ensures that consumers are informed about their rights and the products they purchase. Educational initiatives help consumers understand how to identify fakes and take appropriate action if they encounter counterfeit goods.

By upholding these rights, Consumer Protection Acts empower individuals and foster a fairer marketplace.
4. What role do government agencies play?
Government agencies play a pivotal role in the enforcement of Consumer Protection Acts. They are responsible for creating regulations that govern market practices, ensuring that businesses comply with established standards.
One of the primary functions of these agencies is to investigate complaints from consumers. When a grievance is reported, agencies conduct thorough investigations to determine whether there has been a violation of consumer rights.
In addition, these agencies have the authority to impose penalties on businesses that engage in deceptive practices. Such actions may include fines, sanctions, or even criminal charges against offenders.
Another critical function is consumer education. Government agencies often run campaigns to inform the public about their rights and how to identify counterfeit products. This proactive approach helps to raise awareness and reduce instances of fraud.
Collaboration with other governmental and non-governmental organizations is also vital. Agencies often partner with law enforcement, customs, and international organizations to combat global counterfeiting.

Moreover, these agencies serve as mediators between consumers and businesses, helping to resolve disputes amicably and ensuring that consumer grievances are addressed in a timely manner.
Through these multifaceted roles, government agencies are instrumental in maintaining market integrity and protecting consumers from counterfeit products.
5. How do businesses comply with these acts?
Businesses comply with Consumer Protection Acts through various measures designed to align their practices with legal requirements. Firstly, they must establish internal policies that reflect the standards set by the acts. This includes ensuring product quality, safety, and accurate advertising.
Regular training for employees is also essential. Businesses must educate their staff about consumer rights and the importance of compliance with consumer protection laws.
Moreover, businesses often conduct audits and inspections of their products to ensure they meet safety standards. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they reach consumers.
Transparency in communication is another crucial compliance factor. Businesses should provide clear information about their products, including origins, materials, and any potential risks.
Businesses also engage in consumer feedback mechanisms. By encouraging customers to report issues or concerns, they can address problems promptly and maintain trust with their customer base.

Collaboration with regulatory bodies is essential for compliance. Many businesses work closely with consumer protection agencies to stay updated on legal changes and best practices.
Finally, ethical marketing practices are vital for compliance. Businesses must avoid deceptive advertising and ensure that their marketing accurately reflects the product being sold.
By adhering to these practices, businesses not only comply with Consumer Protection Acts but also foster customer loyalty and trust.
6. What are the penalties for violating these acts?
Violating Consumer Protection Acts can result in severe penalties for businesses. The specific penalties depend on the nature and severity of the violation. Common repercussions include hefty fines, which can be substantial enough to impact a company’s financial standing.
In addition to fines, businesses may face sanctions that limit their operations. These sanctions can include suspension of licenses or permits necessary for conducting business.
In some cases, repeated violations can lead to criminal charges against company executives. This can result in imprisonment, depending on the jurisdiction and the severity of the offense.
Consumer restitution is another possible consequence. Companies may be required to compensate affected consumers for losses incurred due to fraudulent practices.
Additionally, businesses may suffer reputational damage that can have long-term implications. Negative publicity can lead to a loss of customer trust and loyalty, significantly affecting sales and market position.

Compliance audits may also become mandatory, with regulatory agencies closely monitoring businesses for future violations.
Ultimately, the penalties for violating Consumer Protection Acts serve as a critical deterrent against fraudulent practices, promoting a fair marketplace.
7. How can consumers report violations?
Consumers can report violations of Consumer Protection Acts through various channels established by regulatory agencies. Most agencies provide dedicated hotlines or online platforms where individuals can lodge complaints.
When reporting a violation, consumers are typically required to provide detailed information about the issue. This includes specifics about the product, the nature of the complaint, and any relevant documentation or evidence.
It’s also essential for consumers to understand their rights and what constitutes a violation. Many agencies offer resources that outline common violations and how to identify them.
Once a complaint is submitted, regulatory agencies investigate the matter. They may reach out to the business involved for clarification or further information.
Consumers can also engage with consumer advocacy groups, which often assist in the reporting process and provide support to individuals facing difficulties.

Social media platforms have also become a popular venue for consumers to voice their complaints, raising public awareness about unethical practices.
Through these channels, consumers can actively participate in enforcing Consumer Protection Acts, contributing to a safer marketplace for all.
8. What are the challenges in enforcing these acts?
Enforcing Consumer Protection Acts poses several challenges for regulatory agencies. One significant issue is the lack of resources, including funding and personnel, which can limit the capacity to investigate complaints thoroughly.
Additionally, the rapid growth of online marketplaces complicates enforcement efforts. The anonymity and reach of the internet make it easier for counterfeiters to operate, often beyond the jurisdiction of local agencies.
Consumer awareness is another critical challenge. Many individuals are unaware of their rights under these acts, which can result in underreporting of violations and a lack of accountability for businesses.
Furthermore, the legal complexities surrounding consumer protection laws can create barriers to effective enforcement. Different jurisdictions may have varying regulations, making it difficult to apply a consistent approach.

Lastly, cooperation between governmental and non-governmental organizations is essential but can be challenging to achieve. Aligning objectives and strategies across various entities often requires significant coordination and negotiation.
Addressing these challenges is vital for enhancing the effectiveness of Consumer Protection Acts and ensuring robust protection against counterfeit products.
9. How do international laws complement these acts?
International laws play a crucial role in complementing national Consumer Protection Acts. Many countries collaborate through treaties and agreements that aim to standardize consumer protection measures globally. This collaboration is essential in combating cross-border counterfeiting.
International organizations, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), provide frameworks that help nations develop effective consumer protection laws. These frameworks often include guidelines for enforcing standards and sharing information about fraudulent practices.
Moreover, regional agreements, such as those within the European Union, allow for a more integrated approach to consumer protection. By harmonizing laws across member states, these agreements facilitate a unified response to counterfeit goods.

International cooperation also enhances the capacity to investigate and prosecute offenders who operate in multiple jurisdictions. Joint task forces can be established to tackle complex counterfeiting cases that transcend borders.
By complementing national laws with international agreements, countries can create a more robust framework for consumer protection, ultimately leading to safer markets for consumers worldwide.
10. What future trends are expected in consumer protection?
The future of consumer protection is likely to be influenced by several emerging trends. One significant trend is the increasing use of technology in enforcing consumer rights. Advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence can enhance the ability of regulatory agencies to identify patterns of fraud and track down counterfeiters more effectively.
Moreover, as e-commerce continues to grow, consumer protection laws will need to adapt to address the challenges posed by online marketplaces. This may include stricter regulations on online sellers and enhanced consumer education regarding safe online purchasing practices.
Another trend is the growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical consumerism. As consumers become more aware of the social and environmental impacts of their purchases, laws may evolve to ensure that businesses adhere to ethical practices, further protecting consumers from deceptive claims.
Furthermore, international collaboration is expected to strengthen, as countries recognize the importance of working together to combat global issues such as counterfeiting. Sharing best practices and resources will enhance the overall effectiveness of consumer protection efforts.
Ultimately, the evolution of Consumer Protection Acts will reflect the changing landscape of commerce, technology, and consumer expectations, ensuring that consumers remain protected in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Consumer Protection Acts | Laws designed to safeguard consumer rights and prevent unfair trade practices. |
| Prevention of Counterfeits | Regulations on advertising, transparency, inspections, and consumer education. |
| Consumer Rights | Rights include information, safety, choice, and the ability to report violations. |
| Government Agencies | Responsible for enforcement, investigation, education, and consumer support. |
| Business Compliance | Internal policies, training, audits, transparency, and ethical marketing. |
| Penalties for Violations | Fines, sanctions, restitution, and potential criminal charges. |
| Reporting Violations | Channels for lodging complaints include hotlines, online platforms, and advocacy groups. |
| Enforcement Challenges | Resource limitations, online marketplace complexities, and consumer awareness issues. |
| International Laws | Complement national acts and promote cooperation to combat global counterfeiting. |
| Future Trends | Technology use, evolving regulations for e-commerce, and emphasis on sustainability. |


