How Digital Certificates Help Verify Products
1. What Are Digital Certificates and How Do They Function?
Digital certificates act as electronic credentials that prove the authenticity and integrity of information or products. They work similarly to a passport or ID card in the digital space, providing a means to verify an entity’s identity and ensure that the data or product in question is genuine.
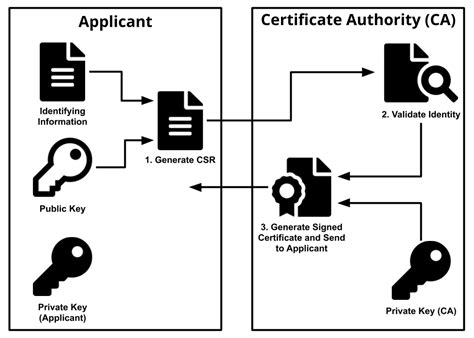
These certificates are issued by a trusted organization known as a Certificate Authority (CA). The CA verifies the identity of the applicant before issuing a certificate, ensuring that the product or service provider can be trusted.
Digital certificates leverage public key infrastructure (PKI), which involves a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is shared openly, while the private key remains confidential. The combination allows for secure encryption and decryption of data.
There are several types of digital certificates, such as:
- SSL/TLS certificates: Used to secure websites by encrypting data transmission.
- Code-signing certificates: Validate the authenticity of software and applications.
- Product certificates: Ensure that a product is original and has not been tampered with.
Digital certificates help confirm that a product or piece of information comes from a trusted source. If the certificate is invalid or expired, users are alerted, reducing the risk of counterfeit or compromised products.

Without digital certificates, it would be difficult to guarantee that products, software, or websites are safe and authentic. These certificates enable users and consumers to have confidence in the security of their transactions and interactions.
In essence, digital certificates create a foundation of trust between manufacturers, service providers, and end-users. They play a critical role in preventing identity theft, fraud, and unauthorized data access.
2. How Do Digital Certificates Ensure Product Authenticity?
Digital certificates are essential tools in combating counterfeit goods. By attaching a certificate to a product, manufacturers provide proof that the item is original and comes from a verified source. Consumers can easily validate the product’s authenticity through the certificate’s details.
For example, many high-end brands use QR codes linked to a digital certificate. Scanning the code allows consumers to access the certificate details, including the manufacturing date, origin, and any associated warranties.
Some key ways certificates ensure authenticity include:
- Encryption: Protects the data embedded within the certificate to prevent tampering.
- Verification: Confirms the product’s identity and origin through a trusted CA.
- Revocation: Invalid certificates are revoked, helping to spot fake products.

The importance of product authenticity cannot be overstated, particularly in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, where counterfeit drugs could be life-threatening. By using digital certificates, companies can protect their brand reputation and safeguard customers from purchasing fake products.
3. What Role Do Certificate Authorities (CAs) Play in Verifying Products?
Certificate Authorities (CAs) are central to the trust model of digital certificates. They are responsible for issuing, validating, and revoking certificates, ensuring that only legitimate entities can use them.
When a CA issues a certificate, it verifies the identity of the applicant thoroughly. This process might include checking business licenses, ownership documents, or other relevant information. The goal is to ensure that the certificate is not issued to fraudulent entities.
In addition to issuing certificates, CAs maintain a certificate revocation list (CRL). This list contains all certificates that have been revoked before their expiration date due to misuse or compromise.
Well-known CAs include organizations like DigiCert, Let’s Encrypt, and GlobalSign. These institutions are widely trusted and recognized, making their certificates highly reliable.
4. How Do Digital Certificates Prevent Counterfeiting?
Counterfeit goods are a significant issue across industries, and digital certificates provide a powerful solution. By digitally signing each product with a certificate, manufacturers ensure that the product is genuine and has not been tampered with during distribution.
The certificate serves as proof that the product is authentic. Consumers or retailers can quickly validate this by scanning the product’s QR code or checking the certificate on the manufacturer’s website.
The certificate’s encryption also ensures that the information cannot be altered by unauthorized parties. If someone tries to modify the product details, the certificate becomes invalid, alerting users to potential fraud.
Another benefit is the traceability provided by certificates. Companies can track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain, identifying any points where tampering or counterfeiting might occur.
Table Summarizing Key Points
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Certificate Authority (CA) | Issues and verifies certificates to confirm product authenticity. |
| Encryption | Protects product data to prevent tampering or forgery. |
| QR Codes | Link products to certificates for easy verification. |
| Traceability | Allows tracking throughout the supply chain. |
FAQ
- What is a digital certificate? A digital certificate is an electronic credential used to verify identity or authenticity.
- How do digital certificates ensure product security? They use encryption and verification processes to prevent tampering.
- Can digital certificates expire? Yes, certificates have expiration dates and must be renewed.
- Who issues digital certificates? Certificate Authorities (CAs) issue and manage them.
- What happens if a certificate is revoked? The product linked to it may be flagged as untrustworthy.
- Are QR codes always used with digital certificates? No, but they are a common method for quick verification.
- How do digital certificates help combat counterfeiting? They provide traceability and ensure only genuine products carry valid certificates.


