How to Recognize Fraudulent Emails: A Comprehensive Guide
1. What Are the Common Signs of a Fraudulent Email?
In today’s digital world, fraudulent emails are a common scam tactic used to deceive recipients. To recognize these emails effectively, understanding the common signs is essential. Here are some indicators:
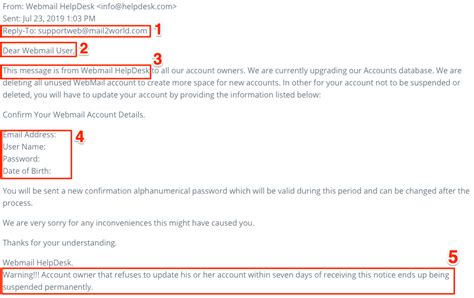
- Suspicious Sender Address: Often, fraudulent emails will have slight variations in the sender’s email address to mimic a legitimate source.
- Urgent Language: Scammers often use language that creates urgency, like “Act Now!” or “Your Account Will Be Closed.”
- Generic Greetings: Many scam emails use generic greetings like “Dear Customer” instead of your actual name.
- Grammar Errors: Fraudulent emails frequently contain typos or unusual grammar.
- Unusual Attachments or Links: Fraud emails often include links to suspicious sites or attachments that may contain malware.
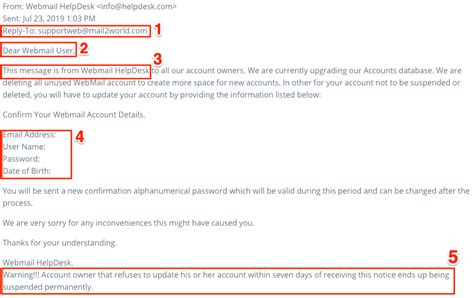
2. How Can I Verify the Sender’s Email Address?
Verifying the sender’s email is a crucial step in avoiding scams. Here’s how:
| Verification Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Check Domain | Ensure the domain matches the legitimate organization’s official domain name. |
| Look for Misspellings | Scam emails often have slight variations or misspellings in the sender’s address. |
| Check SPF and DKIM | These email authentication protocols help confirm legitimate emails. |
3. What Should I Do if an Email Asks for Personal Information?
Legitimate companies rarely request sensitive information through email. Here’s a guide on handling such requests:
- Never Share Personal Details: Avoid providing personal data, like passwords or bank details, through email.
- Use Official Contact Channels: Contact the company directly through official means to verify the request.
- Report the Email: Report suspicious emails to the appropriate authority, such as your email provider or the company’s fraud department.
4. How Can I Identify Suspicious Links in Emails?
Spotting suspicious links is vital. Here are some steps:
- Hover Over Links: Hovering shows the actual URL destination, which should match the sender’s claims.
- Look for HTTPS: Secure websites use HTTPS. Scam links may lack this protocol.
- Shortened URLs: Be cautious with URL shorteners, as scammers often use them to hide the link’s destination.

5. Why Are Grammar and Spelling Errors Red Flags?
Errors in grammar or spelling can be a telltale sign of fraudulent emails, as they often indicate that the sender may not be a native speaker or that the email was hastily constructed.
- Misspellings: Look for small but noticeable misspellings in common words.
- Awkward Phrasing: Fraudulent emails often contain phrases that seem unusual.
- Missing Logos or Incomplete Branding: Legitimate emails typically follow strict branding guidelines.
6. Are There Certain Attachments I Should Avoid Opening?
Attachments are often used in phishing attempts. Follow these tips:
- .exe Files: Avoid executable files, as they may contain malicious software.
- Unexpected Documents: Be cautious if the attachment doesn’t seem relevant to you.
- Encrypted or Password-Protected Files: Fraudsters may use this to bypass email security systems.

7. What Types of Email Phrasing Should I Be Wary Of?
Scam emails often include phrasing that triggers urgency or fear. Here are some examples:
- “Act Now”: This creates a sense of urgency that may lead to quick, uninformed actions.
- “Limited Offer”: Limited offers are used to rush decision-making.
- “Verify Your Account”: This common tactic attempts to gather personal information.
8. How Does Email Spoofing Work, and How Can I Spot It?
Email spoofing is when a scammer disguises themselves as a trusted sender. Here are some common spoofing tactics and how to spot them:
- Check the “Reply-To” Address: Often differs from the “From” address.
- Analyze Header Information: Advanced users can inspect email headers to see the originating IP address.
9. How Do I Report Fraudulent Emails?
Reporting fraudulent emails can protect others. Here’s how:
- Contact Your Email Provider: Most email services have reporting tools for spam or phishing.
- Report to Anti-Phishing Agencies: Organizations like the Anti-Phishing Working Group accept reports.
- Inform Your Bank: If the scam email pertains to banking, inform your bank directly.
10. What Steps Can I Take to Protect Myself from Future Email Scams?
Protecting yourself from scams requires awareness and security measures:
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Adds an extra layer of security to your accounts.
- Update Passwords Regularly: Strong passwords make accounts harder to breach.
- Use Email Filters: Filters can help block potential scam emails.
Summary Table
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Recognizing Signs | Suspicious sender, urgent language, unusual attachments |
| Verifying Sender | Check domain, avoid misspellings |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are phishing emails?
Phishing emails are deceptive emails designed to steal personal information, such as login credentials and financial information.
2. Can email filters help detect fraudulent emails?
Email filters can reduce scam emails by flagging suspicious content or sources.
3. Should I avoid clicking links in all emails?
Always verify the source of links in emails, especially if the sender is unknown or the email looks suspicious.
4. How do spoofing techniques work?
Spoofing involves mimicking a trusted sender to trick recipients into revealing information or clicking harmful links.