How to Use RFID for Verifying Products
1. What is RFID and How Does it Work for Product Verification?
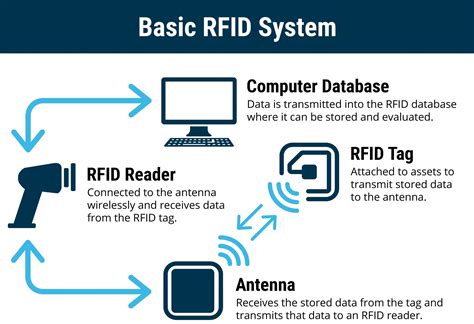
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags store information about the product, which can be read by RFID readers without requiring line of sight. The key components of an RFID system include:
- RFID Tags: These contain a microchip and antenna, storing data about the product. Tags can be passive, active, or semi-passive, depending on their power source.
- RFID Readers: These devices communicate with the tags to retrieve the stored information.
- Antenna: The antenna transmits the radio waves between the reader and the tag.
- Software: This is used to process and manage the data collected from the tags.
Product verification using RFID works by embedding an RFID tag in or on the product packaging. The RFID reader scans the product, retrieves the data stored on the tag, and matches it with the information in the company’s database. This process helps in ensuring product authenticity, reducing counterfeiting, and streamlining supply chain processes.
RFID can be applied in industries like pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and food packaging, where verifying product authenticity is critical. The benefits of RFID for product verification include real-time data tracking, enhanced supply chain management, and improved inventory accuracy.
2. How Can RFID Prevent Counterfeiting in the Supply Chain?
Counterfeiting is a significant challenge in many industries, but RFID can be an effective solution to combat this issue. Here’s how RFID can help:
- Unique Identification: Every RFID tag contains a unique identifier that is difficult to replicate. This provides a layer of security as counterfeiters cannot easily duplicate the tags.
- Track and Trace: RFID allows for real-time tracking of products throughout the supply chain. From the manufacturer to the retailer, every movement can be monitored and verified.
- Product Authentication: By scanning an RFID tag, retailers and consumers can quickly authenticate a product before purchasing.
- Serialized Data: Each RFID tag contains serialized information, ensuring that only genuine products are being handled.
The use of RFID in the supply chain significantly reduces the risk of counterfeit products entering the market. Since each tag is unique, counterfeiters cannot replicate genuine tags or their encoded information. Additionally, RFID technology allows companies to monitor their products’ journey from the factory to the retailer, ensuring authenticity at every stage.
3. What Are the Benefits of Using RFID for Product Verification?
There are numerous benefits of using RFID for product verification:
- Improved Accuracy: RFID provides more accurate tracking compared to barcodes or QR codes. Since RFID tags do not require line of sight, they can be read quickly and accurately in bulk, minimizing errors.
- Enhanced Security: RFID tags contain encrypted information that makes it harder for counterfeiters to tamper with or duplicate.
- Real-Time Monitoring: RFID allows for real-time monitoring of product movement across the supply chain, ensuring that the product’s authenticity is verified at every point.
- Cost Savings: Although the initial cost of implementing RFID may be higher, the long-term savings in labor, time, and inventory management make it a cost-effective solution for businesses.

For companies that deal with high-value goods or those prone to counterfeiting, RFID provides enhanced product security and accountability. The technology not only safeguards products but also helps reduce the time spent on manual inventory checks, resulting in greater efficiency and accuracy in operations.
4. How Can RFID Be Integrated Into Existing Systems?
Integrating RFID technology into existing business systems can be a smooth process with the right planning. Here are the steps:
- Identify Requirements: Businesses need to assess their product verification requirements to determine the type of RFID tags and readers they need.
- Evaluate Current Infrastructure: It is essential to ensure that existing systems can support RFID technology. For example, the warehouse management system (WMS) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) system should be RFID-compatible.
- Choose the Right RFID System: Depending on the environment (warehouse, retail store, etc.), businesses need to choose between passive, active, or semi-passive RFID systems.
- Install Readers and Antennas: Proper installation of readers and antennas is crucial to ensure optimal coverage and accuracy.

Integrating RFID into a company’s existing infrastructure may also require a review of its software systems. Many businesses choose to upgrade their ERP or WMS systems to support RFID data and analytics, enabling real-time insights and enhanced tracking capabilities.
FAQ
1. What is the range of RFID readers?
RFID readers can have a range of a few centimeters to several meters, depending on the type of tag and reader used. Passive RFID readers usually have a shorter range compared to active RFID readers.
2. Can RFID tags be reused?
Yes, RFID tags can be reused depending on the application. Passive RFID tags, which are most common, are typically not reusable, but active RFID tags can be repurposed in certain cases.
3. How secure is RFID technology?
RFID technology is generally secure, especially when encryption is used. However, security risks such as unauthorized scanning or cloning of tags can occur, making encryption and authentication protocols essential for sensitive applications.
4. What industries use RFID for product verification?
Industries such as pharmaceuticals, retail, automotive, and manufacturing use RFID for product verification to combat counterfeiting, manage inventory, and ensure product authenticity.
5. What is the cost of implementing an RFID system?
The cost of implementing an RFID system varies depending on the scale, type of tags, readers, and software required. Initial costs can be high, but the long-term benefits in efficiency and security can outweigh the upfront investment.
6. Can RFID work in harsh environments?
Yes, RFID tags are designed to work in various environments, including harsh conditions like high temperatures, moisture, and exposure to chemicals. Special tags are available for extreme conditions.
7. How does RFID compare to barcodes?
RFID offers several advantages over barcodes, such as the ability to read multiple tags at once, no need for line-of-sight, and the capability to store more data. However, barcodes are still more cost-effective for some applications.