Is Your Sausage Real? How To Identify It
In the realm of food, authenticity is paramount. Consumers increasingly demand to know what’s in their food, particularly when it comes to meat products. Sausage, a beloved culinary staple across cultures, has become a subject of scrutiny, with questions arising about its true composition. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools to confidently identify real sausage and discern its authenticity.
What is Real Sausage?
Real sausage, at its core, is a product crafted from ground meat, typically pork, beef, or lamb. It’s a simple yet versatile preparation, involving blending meat with spices, herbs, and sometimes fillers like bread crumbs or oats. The key characteristic of real sausage is its use of fresh, high-quality meat as the primary ingredient.
The journey from farm to table involves a careful process of meat selection, grinding, seasoning, and stuffing. Real sausage makers prioritize quality, using whole cuts of meat and minimally processed ingredients. This commitment to authenticity ensures that the sausage you enjoy is not only flavorful but also safe and wholesome.
However, the term “sausage” has become increasingly ambiguous. Advancements in food technology have led to the creation of “sausage-like” products that deviate from the traditional definition. These imitations may contain ingredients that are not derived from meat, such as plant-based protein substitutes, fillers, and artificial flavors. Understanding these differences is crucial for discerning real sausage.
How to Identify Real Sausage: A Step-by-Step Guide
Navigating the world of sausages can be daunting, especially with the influx of imitation products. However, with a keen eye and some insider knowledge, you can confidently identify real sausage.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you decipher the truth behind your next sausage purchase:
- Read the Label Carefully: The first step is to carefully inspect the product label. Pay close attention to the ingredient list. Real sausage should primarily consist of meat, such as pork, beef, or lamb. Look for terms like “ground pork,” “ground beef,” or “ground lamb.” Avoid products that list ingredients like “mechanically separated meat,” “textured vegetable protein,” or “soy protein isolate.” These ingredients indicate that the sausage is not entirely meat-based.
- Check the Meat Content: The label should also indicate the percentage of meat content. Look for sausages with a high percentage of meat, ideally above 80%. Lower meat content often suggests the presence of fillers and other additives.
- Scrutinize the Additives: Real sausage typically contains minimal additives. Spices, herbs, and natural flavorings are common additions. Avoid sausages with excessive amounts of preservatives, artificial colors, or flavor enhancers.
- Pay Attention to the Texture: Real sausage should have a firm, slightly springy texture. It should not be overly mushy or have a grainy texture. Examine the sausage casing; it should be smooth and intact.
- Smell the Sausage: Fresh, real sausage should have a pleasant, savory aroma. Avoid sausages that have a sour, rancid, or overly strong smell.
- Seek Out Reputable Brands: Choose sausage from reputable brands that are known for their quality ingredients and traditional methods. Look for brands that emphasize their commitment to sourcing high-quality meat and minimal processing.
- Ask Your Butcher: If you’re unsure about the authenticity of a sausage, don’t hesitate to ask your butcher for guidance. They are experts in meat and can provide insights into the sourcing, processing, and composition of the sausages they sell.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can confidently identify real sausage and enjoy its authentic taste and quality.

What Are the Benefits of Eating Real Sausage?
Beyond its delectable flavor, real sausage offers several nutritional benefits, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Here are some key advantages of consuming authentic sausage:
- Protein Source: Real sausage is a rich source of protein, providing essential amino acids needed for muscle growth, repair, and overall health.
- Iron Content: Sausage contains iron, an important mineral involved in oxygen transport and red blood cell production.
- B Vitamins: Real sausage is a source of B vitamins, which play vital roles in energy metabolism, cell growth, and nerve function.
- Zinc: Sausage provides zinc, a mineral essential for immune function, wound healing, and cell growth.
- Flavor and Versatility: Real sausage adds a delightful depth of flavor to various dishes, ranging from breakfast sandwiches to gourmet dinners.
However, it’s important to note that moderation is key when consuming sausage, as it can be high in fat and sodium. Choosing leaner varieties and preparing sausage with healthy cooking methods can help mitigate these concerns.
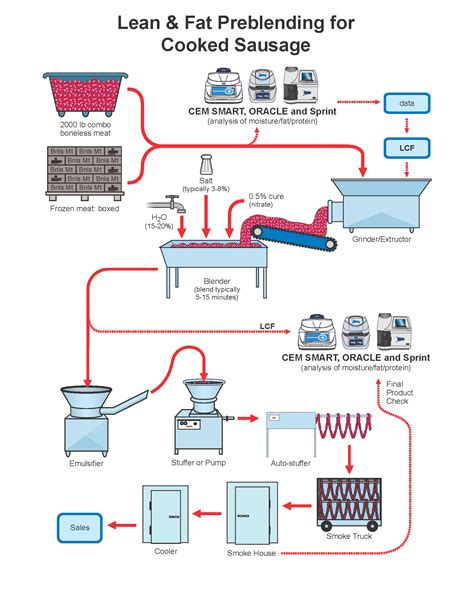
How is Sausage Made?
The process of sausage making is an art form that blends tradition and precision. It begins with the selection of high-quality meat, often pork, beef, or lamb, which is carefully trimmed and ground. The meat is then blended with spices, herbs, and sometimes fillers like bread crumbs or oats. The resulting mixture is carefully stuffed into casings, which are traditionally made from animal intestines but may also be synthetic.
The sausage is then cooked using various methods, including grilling, frying, or baking. The cooking process transforms the raw meat into a flavorful and safe product. Each type of sausage has its unique preparation and flavor profile, reflecting the culinary traditions of its origin.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the sausage-making process:
- Meat Selection: The journey begins with the selection of fresh, high-quality meat, usually from specific cuts like pork shoulder, beef chuck, or lamb shoulder. The meat is inspected for quality and trimmed of excess fat and connective tissues.
- Grinding: The chosen meat is then ground into a fine paste, ensuring even distribution of fat and muscle fibers. The fineness of the grind can vary depending on the desired texture and flavor of the sausage.
- Seasoning: Spices, herbs, salt, and other flavorings are carefully added to the ground meat. The blend of seasonings plays a crucial role in defining the sausage’s flavor profile.
- Stuffing: The seasoned meat mixture is then stuffed into casings, which are traditionally made from animal intestines. Modern techniques also utilize synthetic casings made from collagen or cellulose.
- Cooking: The sausage is then cooked using various methods, such as grilling, frying, or baking. The cooking process ensures the safety of the sausage while also developing its flavor.
The sausage-making process emphasizes the importance of using fresh, high-quality ingredients and traditional methods to create a product that is both flavorful and safe.
What Are the Different Types of Sausage?
The world of sausage is vast and diverse, boasting a wide array of types and flavors. From the classic Italian sausage to the spicy chorizo, each variety offers its unique culinary experience. Here’s an overview of some popular types of sausage:
- Italian Sausage: This popular sausage is typically made from pork, seasoned with fennel, garlic, and red pepper flakes. It’s often used in pasta dishes, pizzas, and sandwiches.
- Bratwurst: Originating from Germany, bratwurst is a type of sausage made from pork and beef, seasoned with spices like nutmeg, ginger, and cardamom. It’s typically grilled or roasted and served with sauerkraut or mustard.
- Chorizo: This spicy sausage originates from Spain and Portugal. It’s made from pork or a blend of pork and beef, seasoned with paprika, garlic, and chili pepper.
- Andouille: Andouille is a smoked sausage from Louisiana, known for its distinctive Cajun flavor. It’s made from pork, seasoned with spices like garlic, cayenne pepper, and paprika. It’s a popular ingredient in gumbo and jambalaya.
- Breakfast Sausage: This sausage is typically made from pork, seasoned with salt, pepper, and sometimes sage. It’s a common breakfast staple, often served with eggs, bacon, or pancakes.
This is just a glimpse into the vast world of sausages. From the classic to the exotic, there’s a sausage for every taste and occasion. Exploring different types of sausage can expand your culinary horizons and introduce you to new flavors and traditions.
How to Store Sausage Properly?
Proper storage is crucial for preserving the quality and freshness of sausage. Here’s a guide on how to store sausage correctly:
- Refrigerator Storage: Uncooked sausage should be stored in the refrigerator at a temperature below 40°F. It’s best to wrap the sausage tightly in plastic wrap or place it in an airtight container to prevent freezer burn and preserve its freshness.
- Freezing: Sausage can be frozen for up to 2-3 months to extend its shelf life. Before freezing, wrap the sausage tightly in plastic wrap or aluminum foil to prevent freezer burn. Frozen sausage can be thawed in the refrigerator overnight before cooking.
By following these storage tips, you can ensure that your sausage remains fresh and flavorful for an extended period.
What Are Some Alternatives to Real Sausage?
While real sausage remains a culinary staple, there are alternative options available for those seeking meat-free or vegetarian alternatives. These alternatives have gained popularity among health-conscious consumers and those with dietary restrictions.
Here are some common alternatives to real sausage:
- Plant-Based Sausages: These sausages are made from plant-based proteins, such as soy, pea protein, or mushrooms. They are often flavored and textured to resemble traditional sausage.
- Vegetarian Sausages: These sausages are made from vegetarian ingredients, such as lentils, beans, or tofu. They may also include spices and herbs to enhance their flavor.
While these alternatives offer a meat-free option, it’s important to note that they may not provide the same nutritional value as real sausage. It’s essential to check the ingredient list and nutritional information to make an informed choice based on your dietary needs and preferences.
Is Your Sausage Real? Conclusion
In a world of culinary innovation and food technology, it’s essential to be discerning consumers. Understanding what constitutes real sausage and how to identify it is crucial for making informed choices about the food we consume. By reading labels, scrutinizing ingredients, and seeking out reputable sources, we can ensure that we are enjoying the authentic taste and quality of real sausage.
Whether you’re a seasoned chef or a home cook, knowing how to identify real sausage will enhance your culinary experience and empower you to make informed choices about the food you eat.
FAQ
What are some signs that a sausage might not be real?
If you see words like “mechanically separated meat,” “textured vegetable protein,” or “soy protein isolate” on the ingredient list, it is likely that the sausage is not made entirely from meat.
Are there any health concerns associated with eating real sausage?
Real sausage is a source of protein, iron, and other nutrients. However, it can also be high in fat and sodium. Choose leaner varieties and prepare sausage with healthy cooking methods to mitigate these concerns.
Is it safe to eat sausage that has been left out at room temperature for a while?
It is not safe to eat sausage that has been left out at room temperature for an extended period, as it can become a breeding ground for bacteria. It’s best to refrigerate sausage promptly after purchasing it.
How do I know if sausage is cooked through?
Cooked sausage should be firm to the touch and have an internal temperature of at least 160°F. The casing should be firm and not feel soft or squishy.
Can I freeze sausage after it has been thawed?
It is not recommended to freeze sausage after it has been thawed, as the texture and quality may be compromised. Thawed sausage should be cooked promptly.
What is the best way to cook sausage?
Sausage can be cooked in various ways, including grilling, frying, baking, or simmering. The cooking method you choose will depend on the type of sausage and the dish you are preparing.
Can I use sausage in vegetarian dishes?
If you are following a vegetarian diet, you can opt for plant-based or vegetarian sausage alternatives that are made without meat.
Summary Table
| Characteristic | Real Sausage | Imitation Sausage |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient List | Primarily consists of meat (pork, beef, lamb) | May contain ingredients like “mechanically separated meat,” “textured vegetable protein,” or “soy protein isolate.” |
| Meat Content | High percentage of meat (ideally above 80%) | Lower meat content, often with fillers and additives |
| Additives | Minimal additives, primarily spices, herbs, and natural flavorings | May contain excessive preservatives, artificial colors, or flavor enhancers |
| Texture | Firm, slightly springy texture; casing is smooth and intact | May be overly mushy or have a grainy texture; casing may be uneven |
| Smell | Pleasant, savory aroma | Sour, rancid, or overly strong smell |
| Source | Reputable brands known for quality ingredients and traditional methods | May be from less reputable brands or unknown sources |



