Spotting Adulterated Cream in Markets: A Comprehensive Guide
What are the Common Signs of Adulterated Cream?
Cream, a rich and flavorful dairy product, is a staple in many cuisines worldwide. However, with increasing cases of adulteration, it’s crucial to know how to spot the signs of adulterated cream. Adulteration can be defined as the deliberate addition of substances to a food product to increase its volume, reduce production costs, or enhance its appearance, often at the expense of quality, safety, and authenticity. Here are some common signs to look out for:
1. Unusual Texture and Consistency: Pure cream should have a smooth, velvety texture and a thick, consistent consistency. Adulterated cream might feel grainy, lumpy, or watery, indicating the addition of substances like starch, gelatin, or water.
2. Abnormal Color and Appearance: Genuine cream should have a pale yellow or white color, depending on the breed of cow and its diet. If the cream appears unusually bright white or has a reddish or yellowish hue, it could be a sign of added dyes or chemicals. Look for any signs of separation or curdling, which could suggest the use of substandard ingredients or improper storage.
3. Unusual Smell and Taste: Pure cream possesses a mild, sweet, and slightly tangy flavor. An overly sweet, artificial taste, or the presence of a bitter, chemical, or pungent smell should raise red flags. These could be signs of added sugars, artificial flavors, or preservatives that compromise the natural taste.
4. Unnatural Stability and Shelf Life: Cream is naturally perishable and has a limited shelf life. If you notice that the cream remains stable for an extended period, without showing any signs of spoilage or separation, it may indicate the addition of preservatives or stabilizers that could affect its quality and nutritional value.
5. Unusual Foam Formation: When whipped, pure cream should produce a thick, stable, and fluffy foam. If the foam collapses quickly or appears watery, it could be a sign of adulteration with additives or low-fat content.
6. Presence of Undissolved Particles: Genuine cream should be free from any visible particles or sediments. The presence of undissolved substances, such as starch granules or gelatin, is a strong indicator of adulteration. You can check this by placing a small amount of cream in a glass and observing it for any particles.
7. Discrepancies in Packaging: Pay close attention to the packaging of the cream. Look for any signs of tampering, damage, or missing information. The label should clearly display the ingredients, expiry date, and other necessary details. Any discrepancies or inconsistencies in the packaging could signal adulteration.
8. Unusual Density and Weight: Pure cream has a specific density and weight. If the cream feels unusually light or heavy for its volume, it could be an indication of adulteration. This can be difficult to determine without specialized equipment but should be considered if other signs of adulteration are present.
9. Price Discrepancies: While it’s essential to be cautious of overly cheap prices, don’t be swayed by exceptionally high prices either. Adulterated cream can be sold at both ends of the price spectrum, so be mindful of both extreme price points.
10. Reputation of the Seller: Always purchase cream from reputable retailers or brands known for their quality and hygiene standards. Check online reviews and consumer feedback to gauge the seller’s reputation and their commitment to providing genuine products.
By being vigilant and aware of these signs, you can protect yourself from buying adulterated cream and ensure you’re consuming a safe and wholesome product.

How Can I Test if Cream is Adulterated at Home?
While sophisticated laboratory tests are required for definitive confirmation, several simple home tests can help you identify potential adulteration in cream. Here are a few methods:
1. Water Dilution Test: Take a small amount of cream in a transparent glass and add a few drops of water. If the cream quickly disperses and mixes evenly with water, it might be adulterated with starch or gelatin. Pure cream will typically maintain its consistency and form a distinct layer on top of the water.
2. Iodine Test: Iodine solution is a simple and effective way to detect the presence of starch, a common adulterant in cream. Add a few drops of iodine solution to a small amount of cream. If the cream turns blue-black, it indicates the presence of starch. Pure cream will not react with iodine and remain its original color.
3. Burning Test: Place a small amount of cream on a clean surface and set it on fire. Pure cream will burn slowly with a pale blue flame, producing a minimal amount of residue. Adulterated cream, particularly those containing starch, will burn rapidly with a bright yellow flame and leave behind a significant amount of ash.
4. Vinegar Test: Add a few drops of vinegar to a small amount of cream. If the cream curdles or forms lumps, it suggests the presence of animal fat or other adulterants. Pure cream will typically remain stable and maintain its consistency.
5. Heat Test: Heat a small amount of cream in a pan over low heat. If the cream separates into layers or forms a thick, sticky residue, it could be adulterated with starch or gelatin. Pure cream will usually heat evenly and maintain its smooth texture.
Important Note: While these tests can provide preliminary insights, they are not definitive. It’s always recommended to consult a certified laboratory for accurate and conclusive results.
What are the Health Risks of Consuming Adulterated Cream?
Consuming adulterated cream can pose various health risks, ranging from mild gastrointestinal discomfort to serious health complications. Here are some of the potential health risks associated with adulterated cream:
1. Food Poisoning: The addition of contaminated water or ingredients can introduce harmful bacteria, such as Salmonella, E. coli, or Listeria, leading to food poisoning. Symptoms of food poisoning include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach cramps, and fever.
2. Allergic Reactions: Adulterated cream may contain substances like gelatin, starch, or artificial flavors that can trigger allergic reactions in individuals with sensitivities to these substances. Allergic reactions can range from mild skin rashes and itching to life-threatening anaphylaxis.
3. Digestive Problems: The use of cheap and substandard ingredients can cause digestive problems like indigestion, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. Adulterants like starch and gelatin can be difficult to digest and can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies: Adulterated cream often contains less fat, protein, and other essential nutrients than genuine cream. This can lead to nutritional deficiencies, particularly in individuals who rely heavily on cream as a source of nutrients.
5. Long-Term Health Issues: The prolonged consumption of adulterated cream can have long-term health implications, including obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. Adulterants like sugars, artificial flavors, and preservatives can contribute to these health problems.
6. Ethical Concerns: Consuming adulterated cream also raises ethical concerns. By purchasing and consuming adulterated products, you are supporting unethical practices and encouraging the exploitation of consumers. It’s important to be aware of these ethical implications and make conscious choices to support ethical and sustainable food practices.
It’s vital to prioritize your health and well-being by choosing genuine and safe cream products. Being informed about the signs of adulteration and taking precautions can help you make informed choices and avoid potential health risks.
What are the Common Adulterants Found in Cream?
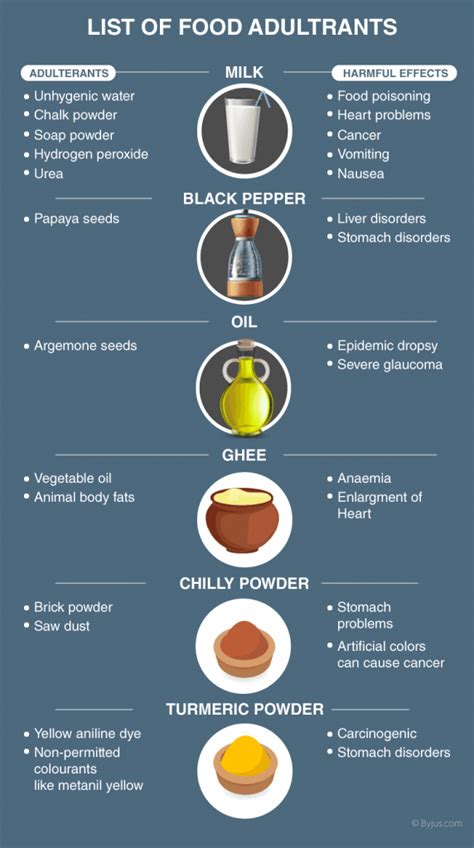
Adulterants used in cream vary widely and depend on the motivations behind the adulteration. Some common adulterants include:
1. Starch: Starch is a common adulterant added to increase the cream’s thickness and volume. It’s cheap and readily available, making it an attractive option for unscrupulous sellers. Starch can be detected by the iodine test, which turns the cream blue-black in the presence of starch.
2. Gelatin: Gelatin is another popular adulterant used to increase cream’s viscosity and stability. It can be extracted from animal bones and hides, making it a cheap and readily available source. Gelatin can be detected by its characteristic jelly-like consistency and by the presence of undissolved particles.
3. Water: Water is often added to dilute the cream, increasing its volume and reducing production costs. It can be detected by the water dilution test, where pure cream should maintain its consistency, while adulterated cream will disperse and mix evenly with water.
4. Sugars: Sugar is added to enhance the sweetness of the cream and mask the taste of adulterants. It can be detected by an overly sweet taste and the presence of undissolved sugar crystals.
5. Artificial Flavors: Artificial flavors are often used to mimic the taste of natural cream and make it more appealing to consumers. These flavors can be detected by an unusual or artificial taste that does not resemble the natural flavor of cream.
6. Preservatives: Preservatives are added to extend the shelf life of cream and prevent spoilage. Common preservatives include sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate, and sorbic acid. These preservatives can be identified by checking the ingredient list on the product label.
7. Vegetable Oils: Some adulterated creams may contain vegetable oils like palm oil or soybean oil to increase their volume and reduce costs. These oils can be detected by their characteristic odor and the presence of undissolved particles.
8. Chemicals: In some cases, adulterated cream may contain harmful chemicals, such as formaldehyde, boric acid, or melamine, which are illegal additives. These chemicals are added to increase shelf life, enhance appearance, or lower production costs. It’s crucial to be aware of these illegal additives and to purchase cream from trusted sources.
Being informed about the common adulterants used in cream can help you identify potential adulteration and make safer purchasing decisions. It’s crucial to exercise caution and to purchase cream from reliable sources to ensure you’re consuming a safe and wholesome product.

What are the Legal Consequences of Selling Adulterated Cream?
Selling adulterated cream is a serious offense with severe legal consequences in many countries. The consequences vary depending on the jurisdiction and the severity of the adulteration, but typically include:
1. Fines: Violators can face hefty fines for selling adulterated cream. The amount of the fine depends on the nature and extent of the adulteration, the amount of cream sold, and other factors.
2. Imprisonment: In some cases, especially for repeated offenses or severe adulteration, violators can face imprisonment. The length of the prison sentence varies depending on the gravity of the offense.
3. Business Closure: Authorities may order the closure of the business involved in selling adulterated cream. This can be a significant setback for the business owner and can lead to financial losses and reputational damage.
4. Product Seizure: Law enforcement agencies can seize the adulterated cream and other products associated with the offense. This can result in significant financial losses for the business owner.
5. Brand Damage: Selling adulterated cream can severely damage the reputation of the brand involved. This can lead to a decline in sales and customer trust, making it difficult for the business to recover.
6. Legal Action: Consumers who suffer health problems due to consuming adulterated cream can take legal action against the seller. This can result in significant financial settlements and further damage the seller’s reputation.
The legal consequences of selling adulterated cream serve as a deterrent to unethical practices in the food industry. It’s crucial for businesses to adhere to food safety standards and ensure that their products are genuine and safe for consumption.
How Can I Protect Myself from Buying Adulterated Cream?
Protecting yourself from buying adulterated cream requires a combination of vigilance, knowledge, and responsible purchasing practices. Here are some effective ways to safeguard yourself:
1. Buy from Reputable Sources: Always purchase cream from established and reputable retailers or brands known for their quality and hygiene standards. Look for well-known brands and avoid unknown or suspicious sellers.
2. Check the Packaging: Inspect the packaging of the cream for any signs of tampering, damage, or missing information. The label should clearly display the ingredients, expiry date, manufacturing date, and other necessary details. Any discrepancies or inconsistencies in the packaging could signal adulteration.
3. Read the Ingredient List: Carefully read the ingredient list on the cream packaging. Look for any unusual or suspicious ingredients, such as starch, gelatin, or artificial flavors. Avoid products with an excessive number of additives or preservatives.
4. Use Your Senses: Use your senses of sight, smell, and taste to evaluate the cream. Pure cream should have a pale yellow or white color, a mild, sweet, and slightly tangy flavor, and a smooth, velvety texture. Any unusual color, smell, or texture should raise red flags.
5. Perform Simple Tests: While not definitive, performing simple home tests like the water dilution test, iodine test, or burning test can help you identify potential adulteration. These tests can provide preliminary insights that can help you make informed decisions.
6. Be Mindful of Price: While overly cheap prices can be a red flag, don’t be swayed by exceptionally high prices either. Adulterated cream can be sold at both ends of the price spectrum, so be mindful of both extreme price points.
7. Report Suspicious Activity: If you suspect that a retailer is selling adulterated cream, report the matter to the local authorities or consumer protection agencies. Your report can help protect other consumers and ensure that the seller is held accountable.
By following these tips and remaining vigilant, you can significantly reduce your risk of buying adulterated cream and ensure you’re consuming a safe and wholesome product.
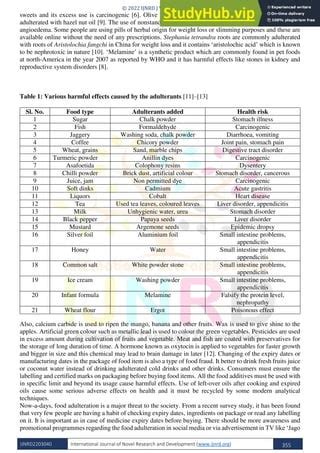
Table Summarizing Information:
| Sign of Adulteration | Description | Test |
|---|---|---|
| Unusual Texture and Consistency | Cream feels grainy, lumpy, or watery. | – |
| Abnormal Color and Appearance | Cream appears unusually bright white, has a reddish or yellowish hue, or shows signs of separation or curdling. | – |
| Unusual Smell and Taste | Cream has an overly sweet, artificial taste, or a bitter, chemical, or pungent smell. | – |
| Unnatural Stability and Shelf Life | Cream remains stable for an extended period without showing signs of spoilage or separation. | – |
| Unusual Foam Formation | Cream produces a weak or watery foam when whipped. | – |
| Presence of Undissolved Particles | Cream contains visible particles or sediments. | – |
| Discrepancies in Packaging | Packaging shows signs of tampering, damage, or missing information. | – |
| Unusual Density and Weight | Cream feels unusually light or heavy for its volume. | – |
| Price Discrepancies | Cream is priced unusually low or high. | – |
| Reputation of the Seller | Seller has a poor reputation or lacks credibility. | – |
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I identify if the cream I bought is adulterated?
While there are no foolproof home tests, you can use several techniques like the iodine test for starch, the burning test for adulterants, or the water dilution test. If you observe any unusual signs like separation, grainy texture, or unpleasant smell, it’s best to discard the cream.
What happens if I consume adulterated cream?
Consuming adulterated cream can lead to various health risks, including food poisoning, allergic reactions, digestive problems, and nutritional deficiencies. It’s crucial to prioritize your health and avoid consuming adulterated products.
Can I report a seller for selling adulterated cream?
Yes, you can report a seller for selling adulterated cream to the local authorities or consumer protection agencies. Providing evidence like pictures, receipts, and details of the seller can be helpful.
Are there any legal consequences for selling adulterated cream?
Yes, selling adulterated cream is a serious offense with severe legal consequences, including fines, imprisonment, business closure, product seizure, and brand damage.
What are the common adulterants found in cream?
Common adulterants include starch, gelatin, water, sugar, artificial flavors, preservatives, vegetable oils, and even harmful chemicals.
Is there a specific type of cream that is more prone to adulteration?
While all types of cream can be adulterated, some types like packaged cream or cream sold in bulk may be more prone to adulteration due to the large volume produced and the potential for cost-cutting measures.
What is the best way to protect myself from buying adulterated cream?
The best way is to buy from reputable sources, carefully inspect the packaging, read the ingredient list, use your senses to evaluate the product, and perform simple home tests.



