What Are Common Examples Of Trending Misinformation?
1. What is Misinformation?
Misinformation refers to false or misleading information spread regardless of intent. It often takes the form of rumors, false news, or misreported facts. In an age of instant communication, the spread of misinformation can happen rapidly through social media, traditional news outlets, and word of mouth.
Understanding misinformation is crucial, as it can influence public opinion, behavior, and decision-making. Misleading information can result in public health crises, political unrest, and social division. Recognizing what constitutes misinformation is the first step in combating its effects.

Misinformation can take various forms. Some examples include:
- False Health Claims: Such as unverified cures for diseases.
- Fake News: Articles that misrepresent facts or events.
- Misleading Statistics: Data presented out of context.
It’s important to critically evaluate the sources of information and verify facts before sharing. This helps to limit the spread of misinformation and its potential impacts.
2. What Are Common Types of Misinformation?
Misinformation can be categorized into several types based on its nature and the context in which it spreads. Here are some common types:
- Health Misinformation: Misleading health claims, especially regarding vaccines and treatments.
- Political Misinformation: False statements or narratives about political figures or events.
- Environmental Misinformation: Incorrect information about climate change and conservation efforts.
Each type has its unique implications and audiences, requiring tailored strategies to counteract. For instance, health misinformation can directly affect public health behaviors, while political misinformation can sway elections.

Identifying these types is essential in understanding the motivations behind misinformation and the means to combat it effectively.
3. How Does Misinformation Spread?
The spread of misinformation occurs through various channels, with social media being a significant contributor. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram allow users to share content rapidly, often without verification.
Factors that facilitate the spread include:
- Viral Sharing: Content that evokes strong emotions tends to be shared more widely.
- Echo Chambers: Users often follow like-minded individuals, amplifying false narratives.
- Algorithm Bias: Social media algorithms favor engaging content, which can include misinformation.
Understanding these mechanisms is critical for developing strategies to combat misinformation online.
4. What Are the Consequences of Misinformation?
The consequences of misinformation can be far-reaching and detrimental. They can affect individuals, communities, and society at large.
Key consequences include:
- Public Health Risks: Misinformation about vaccines can lead to lower vaccination rates, increasing disease outbreaks.
- Political Polarization: False narratives can deepen divides between political groups.
- Economic Impacts: Misinformation can affect market behaviors and investor decisions.
Addressing these consequences requires a concerted effort from governments, media outlets, and individuals to promote accurate information.
5. How Can We Combat Misinformation?
Combating misinformation involves several strategies aimed at promoting accuracy and critical thinking.
- Fact-Checking: Encouraging users to verify information through credible sources.
- Media Literacy Education: Teaching individuals how to critically assess information sources.
- Transparency from Platforms: Social media companies need to take responsibility for the content shared on their sites.
By fostering a culture of skepticism and inquiry, individuals can reduce the likelihood of sharing misinformation.
6. What Role Do Social Media Platforms Play in Misinformation?
Social media platforms play a significant role in the dissemination of misinformation. Their design allows for rapid sharing, often prioritizing engagement over accuracy.
Some measures these platforms have taken include:
- Labeling Misinformation: Adding warnings to content deemed false or misleading.
- Promoting Fact-Checkers: Collaborating with organizations that verify claims.
- Reducing Reach: Limiting the visibility of posts identified as misinformation.
However, the effectiveness of these measures is often debated, with concerns over censorship and the balance between free speech and harmful content.
7. What Are Examples of Misinformation in History?
Historical examples of misinformation show the potential harm of false information. Notable instances include:
- The Tuskegee Syphilis Study: Misleading patients about the nature of their treatment.
- Propaganda during World War II: Misinformation used to sway public opinion and mobilize support.
- Flat Earth Theories: Long-standing misconceptions about the Earth’s shape.
These examples illustrate how misinformation can have lasting effects and highlight the need for vigilance in communication.
8. How Can Individuals Verify Information?
Individuals can take proactive steps to verify information before sharing it. Recommended strategies include:
- Cross-Referencing Sources: Checking multiple sources for consistency.
- Using Fact-Checking Websites: Resources like Snopes or FactCheck.org provide verified information.
- Analyzing the Author’s Credibility: Researching the background of the person or organization behind the information.
By employing these methods, individuals can contribute to a more informed society.
9. What Are the Future Trends in Misinformation?
The landscape of misinformation is continuously evolving, influenced by technological advancements and societal changes.
Future trends may include:
- AI-Generated Content: The rise of artificial intelligence could lead to more sophisticated misinformation.
- Increased Regulation: Governments may implement stricter policies on misinformation dissemination.
- Enhanced Verification Tools: Advances in technology may provide better tools for verifying information.
Staying informed about these trends is crucial for mitigating the impact of misinformation in the future.
10. How Does Misinformation Affect Mental Health?
The impact of misinformation on mental health can be profound, leading to anxiety, stress, and confusion.
Some effects include:
- Increased Anxiety: Exposure to alarming misinformation can heighten feelings of fear.
- Distrust in Media: Repeated exposure to false information can lead to skepticism about all news sources.
- Social Isolation: Misinformation can create divisions, leading to strained relationships.
Addressing these effects requires a focus on mental health resources and support systems.
Summary Table
| Type of Misinformation | Examples | Consequences | Combating Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health | Vaccine misinformation | Public health risks | Fact-checking, media literacy |
| Political | Fake news articles | Political polarization | Transparency from platforms |
| Environmental | Climate change denial | Economic impacts | Public education |
Frequently Asked Questions
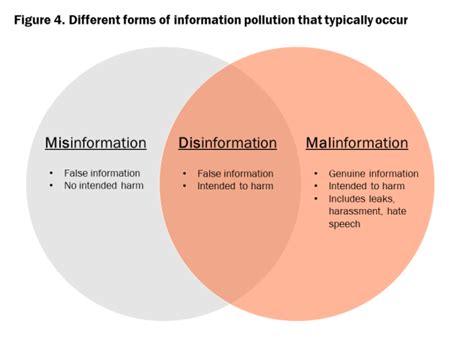
1. What is the difference between misinformation and disinformation?
Misinformation is false information spread without harmful intent, while disinformation is deliberately false information spread with the intent to deceive.
2. How can misinformation affect elections?
Misinformation can sway voter opinions, spread false narratives about candidates, and discourage voter turnout.
3. What role does education play in combating misinformation?
Education fosters critical thinking skills, enabling individuals to assess information more effectively and identify misinformation.
4. Are there specific social media platforms more prone to misinformation?
While all platforms can spread misinformation, those with fewer regulations and algorithms prioritizing engagement, like Facebook and Twitter, are often cited as more problematic.
5. How can businesses address misinformation related to their products?
Businesses can proactively communicate accurate information, engage with customers on social media, and use fact-checking resources to counter misinformation.
6. What impact does misinformation have on public trust?
Widespread misinformation can erode public trust in media, institutions, and scientific research, leading to skepticism and disengagement.
7. How can I report misinformation on social media?
Most social media platforms have reporting tools to flag misinformation. Users can provide context and link to verified information.



