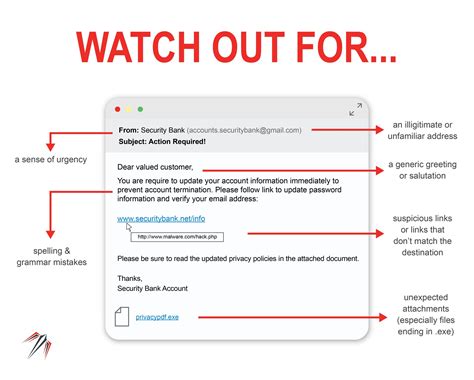
Common Signs of Phishing Emails and How to Protect Yourself
1. What Are the Most Common Signs of a Phishing Email?
Phishing emails often aim to trick recipients into sharing sensitive information. Recognizing these emails can help individuals protect their data. Here are some of the most common signs to watch for:
- Suspicious Sender: Phishing emails often come from unfamiliar or slightly altered email addresses.
- Urgent or Threatening Language: These emails frequently create a sense of urgency to encourage immediate action.
- Grammar and Spelling Errors: Many phishing emails contain noticeable errors.
- Suspicious Links: Hovering over links can reveal URLs that do not match legitimate sites.
- Unexpected Attachments: Be cautious of unsolicited attachments, which may contain malware.
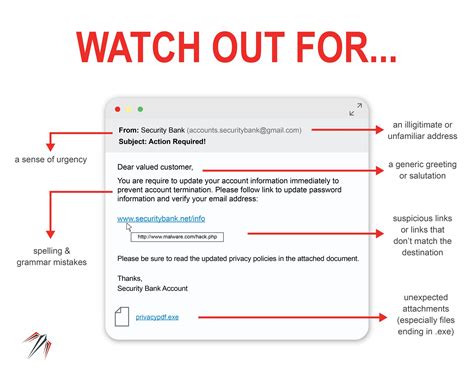
These features can help you detect potential phishing emails, protecting your personal data.
2. How Do Phishing Emails Imitate Legitimate Sources?
Phishing emails often mimic legitimate sources to deceive recipients. Here’s how to identify these imitation tactics:
- Lookalike Domains: Phishing emails may use similar domain names to official organizations (e.g., “security-bank.com” instead of “bank.com”).
- Familiar Logos and Branding: Cybercriminals often include company logos to make the email appear authentic.
- Personalization: Some phishing emails include personal details to enhance credibility.

3. Why Is There Often a Sense of Urgency in Phishing Emails?
Phishing emails often instill a sense of urgency, which pressures recipients to act without thinking. This approach is effective for several reasons:
- Immediate Response: Urgency discourages recipients from verifying information.
- Fear-Based Tactics: Threats like “Your account will be closed” prompt quick action.
4. How Can You Check for Suspicious Links in an Email?
Checking links before clicking is critical. Here’s a guide to analyzing suspicious links:
| Link Check Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Hover Over the Link | Reveals the actual URL destination in the browser’s status bar. |
| Shortened URL Decoders | Use tools to expand shortened URLs. |
| Check for HTTPS | Secure sites start with “https”. |

5. Why Do Phishing Emails Have Spelling and Grammar Errors?
Spelling and grammar mistakes are common in phishing emails for various reasons, often because these messages are mass-produced by international cybercriminals. These mistakes can serve as a red flag.
6. What Should You Do if You Click on a Phishing Link?
If you mistakenly click on a phishing link, take immediate steps to secure your information:
- Run an antivirus scan to detect malware.
- Change any compromised passwords.
7. How Can You Protect Your Personal Information From Phishing Attacks?
Here are some ways to prevent phishing attacks:
- Regularly update passwords.
- Use two-factor authentication.
8. How Do You Report a Phishing Email?
Reporting phishing emails can help prevent further attacks:
- Forward phishing emails to your email provider’s security team.
9. Are Mobile Users More Vulnerable to Phishing?
Mobile users may be at higher risk due to smaller screens and email display limitations. Staying alert is essential.
10. How Can You Train Your Team to Recognize Phishing Emails?
Employee training is crucial. Conduct regular workshops and share the latest phishing tactics to keep your team informed.
Summary Table of Phishing Signs and Actions
| Phishing Sign | Action |
|---|---|
| Suspicious Sender | Verify the sender’s email address. |
| Urgent Tone | Take a moment to review before responding. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is phishing in simple terms?
Phishing is an attempt to trick individuals into providing sensitive information through deceptive emails.
How do I spot a fake email?
Look for signs such as a suspicious sender, errors in grammar, and urgent language.
What should I do if I receive a phishing email?
Do not click on any links; report it to your email provider’s security team.
Can phishing happen on social media?
Yes, phishing can occur through direct messages on social platforms.