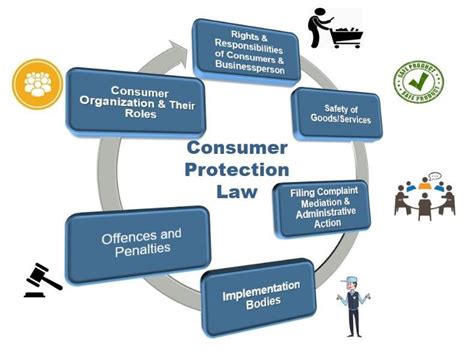
What Are Consumer Protection Laws Against Counterfeits?
Consumer protection laws are designed to protect consumers from counterfeit goods, which include everything from fake electronics to imitation luxury products. These laws vary widely across countries, but their primary goal is to prevent fraud and deception, safeguarding consumers and legitimate businesses. Let’s explore the most critical aspects of consumer protection laws as they relate to counterfeit goods.
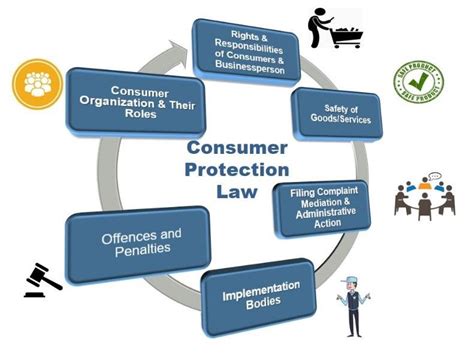
1. Purpose of Consumer Protection Laws
Consumer protection laws are essential in ensuring a fair marketplace by defending the rights of buyers. These laws aim to create a safe environment where consumers can purchase genuine products without the fear of counterfeiting. Additionally, they ensure that companies uphold transparency, particularly in labeling, advertising, and selling goods.
2. Key Legislations Protecting Against Counterfeits
Some of the most significant consumer protection laws worldwide include the Consumer Product Safety Act (CPSA) in the U.S., the EU Consumer Rights Directive, and various Trademark Laws that help in preventing counterfeit sales. The CPSA, for instance, is instrumental in overseeing product safety in the United States, regulating both domestic and imported goods.
3. How Counterfeit Goods Impact Consumers and Brands
Counterfeit products not only affect consumers by providing them with poor-quality items but also harm businesses by undermining brand integrity and sales. For example, a fake smartphone may have compromised safety, potentially leading to injuries. Furthermore, counterfeits erode consumer trust in brands when they encounter poor experiences with imitation products.
4. Measures for Identifying Counterfeit Goods
Consumers can protect themselves by learning how to identify counterfeit goods. Typical signs include inconsistent packaging, spelling errors, and low-quality materials. Many reputable brands also provide online tools where consumers can verify authenticity codes.

5. The Role of Governmental Agencies
Government agencies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) actively work to protect consumers from counterfeits. They conduct regular inspections, monitor online marketplaces, and enforce strict penalties for companies involved in the sale of counterfeit goods.
6. Penalties for Selling Counterfeit Goods
Penalties for counterfeit sales can include fines, lawsuits, and even imprisonment in severe cases. For instance, in the United States, intellectual property laws provide for substantial fines and potential jail time for offenders, depending on the scale and nature of their operations.
7. The Role of E-commerce in Counterfeit Prevention
E-commerce platforms play a critical role in preventing counterfeit sales. Many online marketplaces, such as Amazon and eBay, have dedicated programs to verify seller authenticity and remove counterfeit listings quickly. These platforms also provide channels for consumers to report suspicious products.
8. Consumer Rights and Recourse
Consumers who accidentally purchase counterfeit goods generally have legal recourse. Many countries provide consumers with the right to return or receive compensation for counterfeit products. In cases where the seller refuses to cooperate, consumers can file complaints with regulatory agencies or pursue legal action.

9. Reporting Counterfeit Goods
It’s essential for consumers to report counterfeit goods to help protect others and support regulatory enforcement. Most government agencies offer online forms to report counterfeit sales. Additionally, many brands have hotlines for reporting fake items directly.
10. Future Trends in Counterfeit Protection
The future of counterfeit protection will likely involve more sophisticated technology, such as blockchain and AI, to track and authenticate products. Digital solutions can reduce fraud and counterfeiting, especially as online sales continue to rise. Brands are increasingly adopting these technologies to ensure the integrity of their products.

FAQ
What are consumer protection laws?
Consumer protection laws are regulations designed to protect buyers from unsafe products, fraud, and deceptive practices, including counterfeiting.
How can I identify counterfeit goods?
Look for inconsistencies in packaging, misspellings, and poor-quality materials. Verifying product codes on official brand websites can also help confirm authenticity.
What should I do if I buy a counterfeit product?
If you’ve purchased a counterfeit item, report it to the platform or seller. Many agencies and brands provide channels for compensation or reporting fraud.
What agencies protect against counterfeits?
In the U.S., the FTC and the U.S. Customs and Border Protection, among others, actively enforce laws against counterfeits. In Europe, the EUIPO plays a similar role.
Can I get a refund for a counterfeit product?
In many cases, yes. Consumer protection laws allow buyers to seek compensation, especially if the purchase was through a legitimate retailer.
How does e-commerce impact counterfeit sales?
E-commerce platforms have strict verification policies to combat counterfeiting. Platforms like Amazon monitor sellers and offer reporting channels for counterfeit products.
What penalties exist for selling counterfeits?
Penalties vary but can include fines, imprisonment, and lawsuits. Counterfeit sellers may face severe legal consequences depending on the jurisdiction.