Effective Strategies for Product Verification: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Importance of Product Verification
Product verification is essential in ensuring that a product meets defined specifications and performs reliably in the hands of the end-user. A thorough verification process helps identify design flaws early, minimizes costly production errors, and improves overall product quality.
Verification strategies vary by industry, but certain core principles apply across fields. In this article, we’ll explore key strategies, from risk assessment to test automation, all aimed at helping businesses implement effective and reliable verification processes.
Step 1: Conducting a Risk Assessment for Product Verification
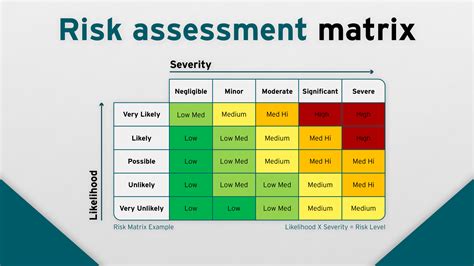
Risk assessment forms the foundation of an effective product verification strategy. By identifying potential areas of failure, companies can prioritize resources and verification efforts, especially in high-risk components.
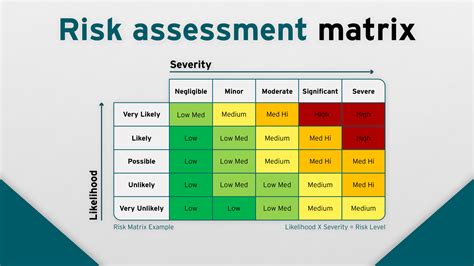
- Identify Risks: Begin by identifying areas where the product may fail.
- Analyze Severity: Rank these risks based on severity, using tools like Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA).
- Plan Resources: Allocate resources to address high-severity risks first, streamlining the verification process.
Establishing clear priorities and strategies in your risk assessment phase is crucial to maintaining a robust verification process, ensuring time and resources are directed toward the areas that matter most.
Step 2: Developing a Verification Plan
A verification plan outlines the goals, scope, and processes necessary to ensure the product’s integrity. This includes defining metrics, selecting testing tools, and establishing timelines.
Components of an effective verification plan include:
- Clear Objectives: Outline the specific outcomes expected from the verification process.
- Resource Allocation: Specify personnel, equipment, and budget needed.
- Test Selection: Choose suitable testing methods based on product complexity.
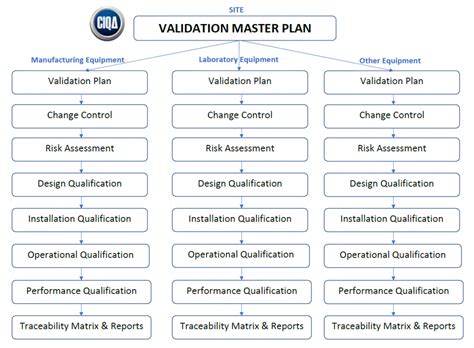
A strong verification plan aligns the entire team, setting clear expectations and providing a roadmap for consistent product verification efforts.
Step 3: Utilizing Test Automation in Product Verification
Automation accelerates the testing process and helps improve consistency. By automating repetitive tests, teams can save time, reduce human error, and allow engineers to focus on more complex tests.
Consider these automation benefits:
- Efficiency: Automated tests execute faster than manual ones, ideal for repetitive checks.
- Consistency: Reduces human error and delivers uniform testing conditions.
Implementing automation requires an initial investment in setup but quickly pays off in terms of time saved and product reliability.
Step 4: Selecting Suitable Testing Methods
The choice of testing method depends on product specifications and potential risks. Types of testing include functional testing, performance testing, and environmental testing.
| Test Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Functional Testing | Ensures product functions as expected | User Interface Testing |
| Performance Testing | Assesses speed, scalability, and stability | Load Testing |
| Environmental Testing | Validates product under various conditions | Temperature Testing |
Selecting the right combination of tests ensures thorough product verification across all usage conditions.
Step 5: Establishing Product Validation Processes
Validation ensures that the final product meets its intended purpose. Unlike verification, which checks if the product is built right, validation ensures it’s the right product for user needs.
Validation involves:
- Field Testing: Real-world testing for usability and durability.
- Feedback Gathering: Surveys or feedback loops with end-users.
Establishing clear validation processes helps confirm that the product will meet end-user expectations effectively.
Step 6: Tracking and Documenting Product Verification Results
Effective documentation provides a record of all tests performed, outcomes, and any adjustments made. Maintaining a log also allows for consistent improvements and quicker troubleshooting.
Essential documentation includes:
- Test descriptions and criteria
- Results and deviations
- Improvement records based on findings
![]()
Comprehensive documentation simplifies the review process and supports quality assurance efforts.
Step 7: Managing Verification with Cross-Functional Collaboration
Product verification benefits from input across engineering, production, and quality assurance teams. Collaborative reviews help identify potential verification gaps early and allow for collective problem-solving.
Encourage collaboration by:
- Involving team members in the planning phase
- Creating regular review checkpoints
- Facilitating open communication on test outcomes
Cross-functional collaboration ensures that verification strategies are holistic and inclusive of multiple perspectives.
Step 8: Adjusting Strategies with Continuous Improvement
Verification is an ongoing process. Continuous improvement allows for adapting and refining methods over time based on findings and changing requirements.
Some effective continuous improvement techniques include:
- Regularly updating verification criteria
- Implementing findings into new product cycles
Continuous improvement ensures that verification processes remain relevant and effective in a dynamic environment.
Step 9: Leveraging Customer Feedback for Verification
Customer feedback offers invaluable insights, especially for consumer products. Analyzing user feedback post-launch helps pinpoint previously unnoticed issues and areas for enhancement.
Step 10: Integrating Quality Standards and Compliance
Compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO) ensures that verification methods align with recognized best practices. Adhering to quality standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and boosts consumer trust.
Summary Table
| Strategy | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Risk Assessment | Prioritize high-risk areas |
| Verification Plan | Outline goals and resources |