The Differences Between Civil and Criminal Penalties for Counterfeiting
1. What Are Civil Penalties for Counterfeiting?
Civil penalties for counterfeiting generally involve financial damages rather than imprisonment. These penalties are imposed to compensate victims and deter future violations.
Civil cases are initiated by private parties or government agencies, aiming to recover damages rather than punish the offender. The burden of proof is lower compared to criminal cases.
Common civil penalties include:
- Monetary damages
- Injunctions against further counterfeiting activities
- Seizure of counterfeit goods
For instance, if a business sells counterfeit products, the original manufacturer can sue for lost profits.
Images of civil penalties in action:

In addition to financial repercussions, civil penalties can also harm the reputation of the infringing party, affecting their business operations.
Understanding the implications of civil penalties helps businesses navigate legal landscapes effectively, fostering a culture of compliance.
2. What Are Criminal Penalties for Counterfeiting?
Criminal penalties are more severe and involve imprisonment or hefty fines imposed by the state. These penalties serve to punish offenders and protect society.
In criminal cases, the government prosecutes individuals, and the burden of proof is higher, requiring evidence of guilt beyond a reasonable doubt.
Types of criminal penalties include:
- Imprisonment
- Fines
- Probation
For example, individuals involved in counterfeiting currency can face significant prison time.

Understanding the distinction between civil and criminal penalties is essential for anyone involved in or affected by counterfeiting.
These penalties highlight the seriousness of counterfeiting as a crime against both individuals and society.
3. How Do Civil and Criminal Penalties Differ in Terms of Burden of Proof?
The burden of proof differs significantly between civil and criminal cases. In civil cases, the plaintiff must demonstrate that their claims are more likely true than not, known as the “preponderance of evidence.”
In contrast, criminal cases require the prosecution to prove the defendant’s guilt “beyond a reasonable doubt,” a much stricter standard.
This difference affects the strategy and outcomes of each type of case.
In civil cases, the lower burden can lead to more successful claims for damages, while the higher burden in criminal cases ensures greater protection for defendants.
Visual representation of the burden of proof:

Legal professionals must adapt their strategies based on these standards to achieve favorable outcomes for their clients.
Overall, understanding these differences is crucial for both plaintiffs and defendants in legal proceedings.
4. What Are the Consequences of Civil Penalties for Businesses?
Civil penalties can have dire consequences for businesses found guilty of counterfeiting. Financial penalties can be significant, impacting a company’s bottom line.
Businesses may also face injunctions, preventing them from engaging in certain practices.
Moreover, reputational damage can deter customers and business partners, leading to long-term financial repercussions.
For example, a company involved in selling counterfeit goods may lose customer trust, impacting sales.
Businesses must ensure compliance with intellectual property laws to avoid these severe consequences.

Legal costs associated with defending against civil suits can further strain financial resources.
Effective compliance programs can help mitigate the risk of civil penalties.
5. How Do Criminal Penalties Affect Individuals Involved in Counterfeiting?
Individuals convicted of counterfeiting face serious criminal penalties, including imprisonment and fines. These consequences can disrupt their personal and professional lives.
A criminal record can hinder future employment opportunities, impacting long-term financial stability.
For example, someone convicted of counterfeiting may struggle to find jobs that require background checks.
In addition to legal repercussions, the personal toll can be significant, leading to stress and familial strain.
Understanding the potential consequences can deter individuals from engaging in counterfeiting activities.
6. How Are Penalties Determined in Counterfeiting Cases?
The determination of penalties in counterfeiting cases depends on several factors, including the severity of the offense, the defendant’s criminal history, and the impact on victims.
Courts may consider aggravating factors, such as the scale of counterfeiting or whether the offense involved organized crime.
A table summarizing factors influencing penalty severity:
| Factor | Impact on Penalty |
|---|---|
| Severity of Offense | Higher severity leads to harsher penalties |
| Criminal History | Repeat offenders face stiffer penalties |
| Impact on Victims | Greater harm leads to increased penalties |
Judges have discretion in sentencing, allowing them to consider individual circumstances.
Ultimately, understanding these factors can help individuals and businesses navigate the legal landscape more effectively.
7. What Role Do Regulatory Agencies Play in Counterfeiting Cases?
Regulatory agencies, such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Department of Justice (DOJ), play crucial roles in combating counterfeiting.
These agencies investigate counterfeiting cases, enforce laws, and provide guidance to businesses on compliance.
They may also engage in public awareness campaigns to educate consumers about the risks of counterfeit goods.
Images representing regulatory efforts:
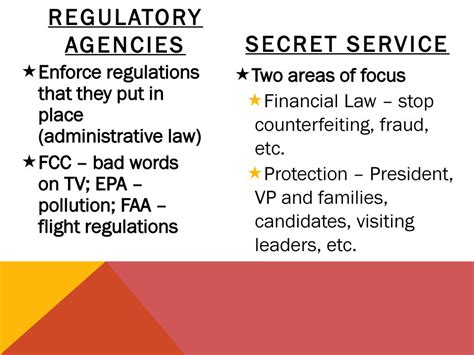
By collaborating with law enforcement and businesses, these agencies aim to reduce the prevalence of counterfeiting in the marketplace.
Understanding the role of regulatory agencies can help individuals and businesses stay informed about compliance requirements.
8. How Do International Laws Address Counterfeiting?
International laws play a significant role in addressing counterfeiting, especially in a globalized economy.
Various treaties and agreements, such as the Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS), establish standards for intellectual property protection.
Countries may cooperate to enforce these laws, leading to cross-border actions against counterfeiters.
Images illustrating international efforts against counterfeiting:

Understanding international laws helps businesses navigate the complexities of global trade and intellectual property rights.
It also highlights the importance of compliance across jurisdictions.
9. What Are the Long-Term Implications of Counterfeiting on the Economy?
Counterfeiting has significant long-term implications for the economy, including loss of revenue for legitimate businesses and tax losses for governments.
The presence of counterfeit goods can undermine consumer confidence, affecting market stability.
Moreover, industries may suffer from reduced innovation as businesses shy away from investing in new products.
Images depicting the economic impact of counterfeiting:

Understanding these implications can motivate businesses and governments to take proactive measures against counterfeiting.
10. How Can Businesses Protect Themselves Against Counterfeiting?
Businesses can take several steps to protect themselves against counterfeiting, including implementing robust compliance programs, educating employees, and monitoring the marketplace for counterfeit goods.
They can also engage in collaborations with law enforcement and regulatory agencies to report and address counterfeiting effectively.
Images representing business protections against counterfeiting:

By adopting proactive measures, businesses can safeguard their interests and contribute to a healthier marketplace.
Summary of Key Points
| Aspect | Civil Penalties | Criminal Penalties |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Compensation for victims | Punishment of offenders |
| Burden of Proof | Preponderance of evidence | Beyond a reasonable doubt |
| Consequences | Monetary damages, injunctions | Imprisonment, fines |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is counterfeiting?
2. What types of products are commonly counterfeited?
3. How can consumers identify counterfeit products?
4. What should I do if I encounter counterfeit goods?
5. Are there specific laws against counterfeiting?
6. How does counterfeiting impact the economy?
7. What resources are available for businesses facing counterfeiting issues?


