What Are the Risks of Counterfeiting?
Counterfeiting poses significant risks across various sectors, impacting economies, consumers, and businesses alike. The consequences can be far-reaching, affecting everything from product safety to brand integrity.
One major risk associated with counterfeiting is the potential harm to consumers. Counterfeit products, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals, automotive parts, and electronics, can be substandard or even dangerous. For example, counterfeit medications may not contain the correct active ingredients, leading to ineffective treatment or adverse reactions.
Moreover, counterfeit goods can erode consumer trust in legitimate brands. When consumers unknowingly purchase fake products, they may associate negative experiences with the original brand, damaging its reputation. This trust deficit can lead to decreased sales and long-term brand loyalty issues.
In addition, counterfeiting can have significant economic implications. Industries affected by counterfeiting often experience revenue losses, which can lead to job cuts and decreased investments in innovation. The global economy suffers as counterfeit operations evade taxes and stifle legitimate businesses.
From a legal standpoint, counterfeiting also poses risks. Businesses that fall victim to counterfeiting may face challenges in protecting their intellectual property. This often requires costly legal action, diverting resources from other important business activities.
Counterfeiting can also contribute to organized crime and corruption. The illicit trade of counterfeit goods can finance criminal enterprises, further perpetuating cycles of crime and violence in affected communities. This connection underscores the broader societal implications of counterfeiting.
To combat counterfeiting, companies can implement advanced technologies, such as blockchain and RFID tags, to ensure product authenticity. These measures help secure the supply chain and reassure consumers about the legitimacy of their purchases.
Additionally, educating consumers about the risks of counterfeiting is crucial. By raising awareness, consumers can make informed choices and recognize the signs of counterfeit products. This grassroots effort can create a culture of vigilance against counterfeiting.
Governments also play a role in mitigating counterfeiting risks. Stricter enforcement of intellectual property laws and collaboration with businesses can lead to more effective crackdowns on counterfeit operations.
Ultimately, the risks of counterfeiting affect everyone, and addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that involves businesses, consumers, and governments.

How Does Counterfeiting Affect Brand Integrity?
Brand integrity is critical for businesses, and counterfeiting poses a direct threat to this essential asset. When counterfeit products flood the market, they can significantly tarnish the image of legitimate brands.
One primary way counterfeiting affects brand integrity is through compromised quality. Consumers expect certain standards from brands, and when counterfeit versions fail to meet these expectations, it reflects poorly on the original brand. For instance, if a luxury fashion brand is associated with low-quality counterfeit goods, it diminishes its perceived value.
Additionally, the proliferation of counterfeit products can confuse consumers about what is genuine. This ambiguity can lead to customers purchasing fake items, thinking they are legitimate. Such experiences can result in a loss of customer trust and loyalty.
Counterfeiting also allows competitors to capitalize on a brand’s reputation without incurring the same costs. This unfair competition undermines the investments made by legitimate businesses in marketing and product development.
Legal battles often ensue as brands attempt to protect their integrity. This can be an exhausting process that drains resources and detracts from a company’s ability to focus on core business activities.
Furthermore, brands may be forced to alter their marketing strategies in response to counterfeiting threats. They may need to increase security measures or develop new branding approaches to distinguish genuine products from fakes, which can disrupt their established identity.
Investing in anti-counterfeiting technologies, such as holograms or unique identifiers, can help preserve brand integrity. These methods reassure consumers and deter counterfeiters.
Consumer education is also vital. By informing customers about how to identify genuine products, brands can empower them to make informed decisions, thereby protecting their integrity.
Brands must also engage with regulatory bodies to advocate for stronger enforcement against counterfeiting. Collaboration can enhance the effectiveness of measures designed to protect brand integrity.
Ultimately, counterfeiting presents a substantial threat to brand integrity, making proactive measures essential for businesses to safeguard their reputations.

What Industries Are Most Affected by Counterfeiting?
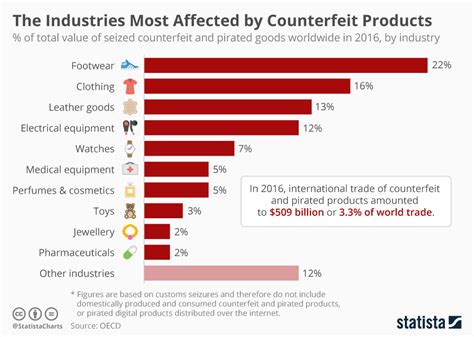
Counterfeiting affects various industries, but some sectors experience a more significant impact than others. Understanding which industries are most affected can help in developing targeted strategies to combat counterfeiting.
The fashion industry is one of the most commonly impacted by counterfeiting. High-end brands often find themselves facing a barrage of counterfeit products that mimic their designs. This not only leads to financial losses but also affects brand reputation.
The electronics sector is another area heavily affected by counterfeiting. Fake components can find their way into legitimate products, leading to safety concerns and potential product failures. The financial implications for manufacturers can be severe.
Pharmaceuticals are perhaps the most critical industry when it comes to counterfeiting risks. Fake medications can pose serious health risks to consumers. The World Health Organization estimates that up to 10% of medicines in low- and middle-income countries are counterfeit, highlighting the urgency of the issue.
Automotive parts are also a target for counterfeiters. Fake components can compromise vehicle safety, leading to potentially disastrous outcomes for consumers and manufacturers alike. The automotive industry must remain vigilant to protect both consumers and their reputations.
The luxury goods market, encompassing jewelry, watches, and accessories, suffers significantly from counterfeiting. The value associated with luxury brands makes them prime targets for counterfeiters aiming to exploit their reputation.
Counterfeiting also extends to software and digital goods. Pirated software not only affects revenue for legitimate companies but can also lead to security vulnerabilities for users who unknowingly install counterfeit programs.
Cosmetics and personal care products are increasingly being targeted by counterfeiters. These products can pose health risks, especially if they contain harmful substances, further endangering consumers.
Counterfeit goods in the food and beverage industry can have dire consequences, leading to health risks and loss of consumer confidence in brands. Counterfeit food products can mislead consumers about quality and origin.
Ultimately, understanding which industries are most affected by counterfeiting allows for the development of focused strategies to combat the issue, ensuring that businesses and consumers are better protected.
What Are the Economic Impacts of Counterfeiting?
Counterfeiting has profound economic implications that extend beyond individual businesses to affect entire industries and economies. Understanding these impacts is crucial for stakeholders seeking to mitigate risks.
One of the most immediate economic effects of counterfeiting is the loss of revenue for legitimate businesses. When consumers opt for counterfeit products, it directly impacts sales for original brands, leading to significant financial losses.
Counterfeiting also stifles innovation. When businesses face the threat of counterfeit goods, they may be less inclined to invest in research and development. This stagnation can hinder technological advancements and overall economic growth.
The job market can suffer as well. Companies affected by counterfeiting may resort to layoffs or hiring freezes due to decreased revenue. This can create a ripple effect throughout the economy, impacting suppliers and service providers.
Counterfeit goods often evade taxes, leading to reduced government revenue. This loss can hinder public services and infrastructure development, impacting society as a whole.
Moreover, counterfeiting can create unfair competition. Legitimate businesses that invest in quality and safety may find it challenging to compete against low-cost counterfeit products, leading to market distortions.
Counterfeit operations can also contribute to organized crime, diverting funds from legitimate economic activities. This connection can have broader implications for societal stability and security.
Investing in anti-counterfeiting measures can incur costs for businesses. However, these investments are often outweighed by the potential losses associated with counterfeiting. Companies must weigh the costs and benefits of protective measures to safeguard their interests.
The overall economic impact of counterfeiting can be quantified in terms of lost jobs, revenue, and innovation. A coordinated response involving businesses, consumers, and governments is essential to address these economic challenges effectively.
Ultimately, understanding the economic implications of counterfeiting is vital for developing comprehensive strategies that protect businesses and bolster the economy.



