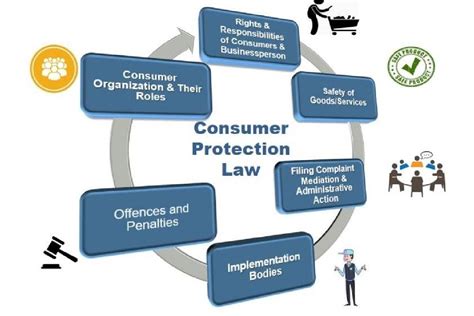
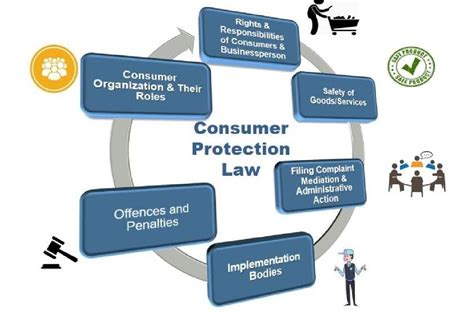
Understanding Consumer Protection Laws: Key Insights and FAQ
1. What is the Purpose of Consumer Protection Laws?
Consumer protection laws are designed to safeguard buyers against unfair, deceptive, or fraudulent practices in the marketplace. These regulations ensure that businesses engage in fair trade, provide safe products, and offer transparent services. The goal is to create a level playing field where consumers are informed and treated ethically.
- Transparency: Businesses must provide clear information about products and services.
- Fair Practices: Companies are prohibited from using deceptive advertising or sales tactics.
- Product Safety: Regulations ensure that items meet safety standards to prevent harm to consumers.
In many countries, consumer protection laws cover areas like:
| Area | Example |
|---|---|
| Product Quality | Ensuring items meet minimum quality and durability standards. |
| Refund Policies | Providing consumers with the right to return or exchange defective products. |
| Privacy Rights | Regulations regarding the handling and protection of personal information. |
2. How Do Consumer Protection Laws Vary Globally?
Different countries enforce varying levels of consumer protection. For instance, in the European Union, consumer rights are highly standardized, while in other regions, these laws can vary widely depending on local policies. Some nations focus heavily on product safety, whereas others may emphasize financial transaction security or data privacy.
Key global differences include:
- Refund Policies – E.U. mandates a two-week cooling-off period for most purchases, unlike the U.S.
- Product Safety Standards – Standards may vary significantly by country, impacting product availability.
- Data Protection – GDPR in the E.U. vs. varying privacy laws in other regions.

3. What are the Main Consumer Rights Protected by Law?
Consumer rights typically include:
- The right to safety.
- The right to be informed.
- The right to choose.
- The right to be heard.
- The right to satisfaction of basic needs.
- The right to redress.
- The right to consumer education.
Each right plays a vital role in maintaining a balanced marketplace and ensuring consumer satisfaction. By upholding these rights, consumer protection laws prevent unethical practices and promote transparency.

FAQ
What is the main purpose of consumer protection laws?
The main purpose is to protect consumers from unfair practices, ensure product safety, and promote transparency in the marketplace.
How do consumer protection laws impact businesses?
These laws require businesses to maintain ethical standards, provide accurate product information, and handle customer complaints responsibly.
What are some examples of consumer rights?
Examples include the right to safety, the right to be informed, and the right to redress, which allow consumers to be protected and informed in their transactions.
How do consumer protection laws vary by country?
Consumer protection laws vary widely, with regions like the E.U. having standardized laws, while others may have fewer protections or varying policies.
What role do agencies play in enforcing consumer protection laws?
Agencies like the FTC in the U.S. and the European Consumer Centre in the E.U. monitor compliance and address complaints from consumers.
Can consumer protection laws impact online shopping?
Yes, these laws impact online transactions by ensuring safe payment options, privacy protections, and clear return policies.
How can consumers file a complaint under these laws?
Consumers can contact relevant agencies, such as the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, or use online forms to file complaints about unfair practices.