Understanding the Product Lifecycle Concerning Counterfeiting
1. What is the product lifecycle, and how does it relate to counterfeiting?
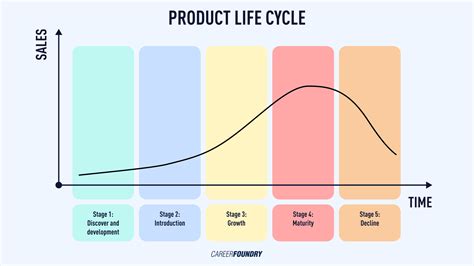
The product lifecycle refers to the stages a product goes through from inception to decline. These stages include introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Understanding this lifecycle is crucial for businesses to manage counterfeiting effectively. Each stage presents unique challenges and opportunities for counterfeiters.
In the introduction phase, a new product is launched, often attracting the attention of counterfeiters eager to exploit consumer curiosity. Companies must focus on building brand awareness and trust.
During the growth stage, sales increase, making products more appealing to counterfeiters. Effective branding and protection strategies are vital to safeguard intellectual property.
In the maturity phase, competition intensifies, leading to potential price erosion. Here, counterfeiting can significantly impact profits. Businesses need to adopt robust anti-counterfeiting measures.
Finally, in the decline stage, products may be less targeted, but counterfeiting can still pose risks. Companies should evaluate their product portfolio and consider phasing out vulnerable products.
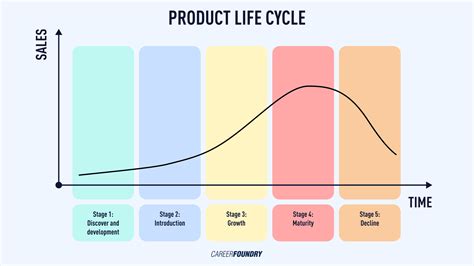
Overall, the product lifecycle stages provide a framework for understanding how counterfeiting can evolve and what measures can be taken at each phase to mitigate risks.
2. How can businesses protect themselves from counterfeiting throughout the product lifecycle?
Businesses can implement various strategies to protect themselves from counterfeiting at each stage of the product lifecycle. A comprehensive approach combines legal, technological, and marketing tactics.
In the introduction phase, companies should secure trademarks and patents to legally protect their innovations. Early registration is crucial to deter counterfeiters.
During the growth phase, businesses can invest in brand education campaigns to inform consumers about genuine products. Clear communication helps build consumer trust and recognition.
In the maturity stage, organizations might consider using advanced technologies such as holograms or QR codes that verify authenticity. These tools can significantly reduce the chances of counterfeiting.
Finally, in the decline stage, firms should analyze data on counterfeit incidents to refine their strategies and decide whether to discontinue vulnerable products or rebrand.

By proactively addressing counterfeiting risks throughout the product lifecycle, businesses can safeguard their brands and revenues.
3. What are the most common types of counterfeit products seen in different lifecycle stages?
Counterfeit products vary across different lifecycle stages, reflecting consumer demand and market trends.
- Introduction Stage: Fake versions of trendy gadgets often appear, targeting early adopters.
- Growth Stage: Popular fashion items, electronics, and luxury goods are commonly counterfeited as their popularity soars.
- Maturity Stage: Brands face competition from both legitimate and counterfeit versions of their products, leading to a diverse range of fakes.
- Decline Stage: Older products may still see counterfeits, but they tend to be less sophisticated.

Understanding the common counterfeit products at each lifecycle stage helps businesses anticipate threats and take preventative measures.
4. How does consumer awareness influence counterfeiting during the product lifecycle?
Consumer awareness plays a pivotal role in combating counterfeiting. Educated consumers are less likely to purchase counterfeit goods.
In the introduction phase, companies can leverage social media to educate consumers about their brand and products, building initial trust and recognition.
As a product enters the growth stage, increasing consumer knowledge about counterfeiting can deter potential buyers from purchasing fakes.
During the maturity stage, strong consumer awareness campaigns highlighting the dangers of counterfeits can lead to greater vigilance.
Even in the decline phase, maintaining consumer awareness can help protect a brand’s reputation and discourage counterfeit purchases.

Ultimately, a well-informed consumer base can significantly diminish the impact of counterfeiting throughout the product lifecycle.
5. What role does technology play in combating counterfeiting in the product lifecycle?
Technology is a crucial ally in the fight against counterfeiting. Various technological solutions can be implemented throughout the product lifecycle.
In the introduction phase, blockchain technology can help track a product’s origin, ensuring authenticity right from the start.
During the growth stage, businesses can utilize RFID tags and IoT devices to monitor products in real-time, providing a secure supply chain.
In the maturity phase, advanced authentication methods, such as biometric verification, can enhance security against counterfeiting.
Even in the decline stage, technology can assist in analyzing counterfeit trends, allowing businesses to adapt their strategies effectively.

By integrating technology into their anti-counterfeiting strategies, businesses can safeguard their products more effectively throughout the lifecycle.
6. How do regulatory frameworks impact counterfeiting and the product lifecycle?
Regulatory frameworks significantly influence the landscape of counterfeiting. They provide legal protection and guidelines for businesses to follow.
In the introduction phase, strong intellectual property laws can deter counterfeiters from entering the market.
As products grow in popularity during the growth stage, effective enforcement of these laws becomes critical in combating counterfeiting.
In the maturity stage, businesses often rely on regulatory bodies to help monitor and control counterfeit activity, ensuring market integrity.
Even in the decline stage, established regulations can assist companies in transitioning their products responsibly and protecting remaining brand equity.
Thus, a robust regulatory environment can provide businesses with the tools necessary to combat counterfeiting effectively.
7. What impact does counterfeiting have on brand reputation throughout the product lifecycle?
Counterfeiting poses serious risks to brand reputation, affecting consumer perception and loyalty.
During the introduction phase, counterfeit products can confuse consumers, leading to a lack of trust in the brand’s authenticity.
As the product enters the growth stage, negative experiences with fakes can tarnish a brand’s image, affecting sales.
In the maturity stage, persistent counterfeiting can erode consumer confidence, making it challenging for brands to maintain market share.
In the decline stage, a tarnished reputation can hinder efforts to rejuvenate the brand or launch new products.
Thus, brands must prioritize measures to combat counterfeiting to preserve their reputation throughout the product lifecycle.
8. How does globalization affect counterfeiting in the product lifecycle?
Globalization has profound implications for counterfeiting, as it opens markets but also increases exposure to counterfeit goods.
In the introduction phase, global launch strategies must consider potential counterfeit risks in diverse markets.
During the growth stage, companies must navigate international laws and regulations, which can vary widely, complicating enforcement against fakes.
In the maturity stage, the proliferation of online marketplaces increases the likelihood of counterfeits reaching consumers.
Even in the decline stage, global networks can facilitate the spread of counterfeit goods, necessitating continuous vigilance.

Therefore, understanding globalization’s role in counterfeiting is essential for businesses looking to protect their products globally.
9. What strategies can consumers adopt to avoid counterfeit products throughout the product lifecycle?
Consumers can play a significant role in combating counterfeiting by adopting informed purchasing strategies.
In the introduction phase, consumers should research new products and only purchase from authorized retailers.
During the growth stage, they can look for quality indicators such as packaging details and authenticity labels.
In the maturity stage, being vigilant about pricing can help consumers avoid deals that seem too good to be true.
Even in the decline stage, consumers should remain cautious and report suspicious products to help protect others.

By staying informed and vigilant, consumers can help reduce the prevalence of counterfeiting in the marketplace.
10. How can companies adapt their marketing strategies to address counterfeiting risks during the product lifecycle?
Companies can enhance their marketing strategies to mitigate the risks associated with counterfeiting at each lifecycle stage.
In the introduction phase, creating buzz around a product can help consumers distinguish between genuine and counterfeit offerings.
During the growth stage, brands can leverage social media and influencer partnerships to build authentic connections with consumers.
In the maturity stage, marketing campaigns highlighting the dangers of counterfeiting can further educate consumers.
In the decline stage, rebranding or repositioning strategies can refresh a brand’s image and distance it from counterfeit associations.

By adapting marketing strategies to address counterfeiting risks, companies can protect their brand integrity throughout the product lifecycle.
Summary Table
| Lifecycle Stage | Counterfeiting Risks | Protection Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | High exposure to fakes | Secure trademarks, educate consumers |
| Growth | Increased counterfeit activity | Brand campaigns, advanced authentication |
| Maturity | Competitive pressure | Enhanced monitoring, regulatory support |
| Decline | Residual counterfeit presence | Data analysis, phased product strategies |
FAQs
1. What is the impact of counterfeiting on consumer trust?
Counterfeiting can significantly undermine consumer trust in a brand, leading to lost sales and damaged reputation.
2. How can consumers identify counterfeit products?
Consumers can look for quality indicators, check packaging, and verify purchase sources to identify counterfeits.
3. What legal measures can companies take against counterfeiters?
Companies can pursue trademark registration, file lawsuits, and collaborate with law enforcement to combat counterfeiting.
4. Are there industries more susceptible to counterfeiting than others?
Yes, luxury goods, pharmaceuticals, and electronics often face higher rates of counterfeiting due to high demand.
5. How do online marketplaces contribute to counterfeiting?
Online marketplaces can facilitate the sale of counterfeit goods, making it easier for counterfeiters to reach consumers.
6. What are the long-term effects of counterfeiting on businesses?
Long-term effects can include reduced sales, damaged brand reputation, and increased costs for anti-counterfeiting measures.
7. How can businesses effectively collaborate with authorities to combat counterfeiting?
Businesses can share intelligence, report counterfeit activity, and participate in industry coalitions focused on anti-counterfeiting efforts.