Understanding Legislative Changes in Counterfeiting Prevention
1. What Are the Key Legislative Frameworks Addressing Counterfeiting Prevention?
Counterfeiting impacts industries worldwide, undermining intellectual property rights, economies, and consumer safety. Various legislative frameworks have been established globally to address this challenge. This section covers the primary legislation guiding counterfeiting prevention, including examples of laws, regulations, and the responsible agencies in different regions.

Key legislative frameworks include:
- The TRIPS Agreement: This agreement from the World Trade Organization requires member countries to enforce minimum standards for intellectual property protection.
- EU Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) Enforcement Directive: This directive establishes the EU’s strategy for intellectual property rights enforcement.
- Lanham Act (United States): Protects trademarks to ensure authenticity and prevent consumer confusion.
2. How Do Anti-Counterfeiting Laws Differ Across Regions?
The approach to counterfeiting varies across different regions, influenced by cultural, legal, and economic factors. While Europe and the U.S. have stringent intellectual property laws, other regions may prioritize enforcement differently. This section compares these regional differences in anti-counterfeiting laws.
Here’s a comparison of anti-counterfeiting measures across major regions:
| Region | Key Legislation | Enforcement Agency |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Lanham Act, Customs and Border Protection Act | U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) |
| European Union | EUIPO Enforcement Directive | European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) |
| China | Trademark Law, Patent Law | National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA) |
3. How Does Technology Enhance Legislative Enforcement Against Counterfeiting?
Technological advancements play a significant role in supporting legislation by enhancing tracking, verification, and reporting processes. Governments leverage technologies like blockchain and artificial intelligence to aid in enforcement and to create transparency in supply chains.
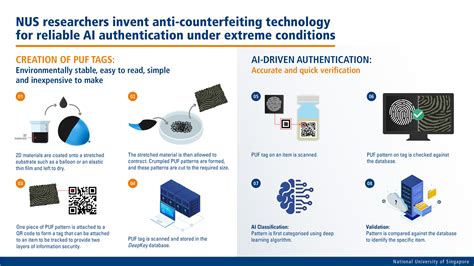
Technologies aiding anti-counterfeiting efforts include:
- Blockchain: Provides a tamper-proof ledger to verify the origin and authenticity of goods.
- AI-Based Image Recognition: Assists in identifying counterfeit logos or trademarks online.
- RFID and QR Codes: Allow real-time tracking of product movement through supply chains.
4. What Is the Impact of the EU Digital Services Act on Counterfeiting?
The EU Digital Services Act (DSA) establishes strict rules for online platforms to control counterfeit goods. This act obliges platforms to detect and remove counterfeits proactively, potentially changing the landscape for online marketplaces.

Key aspects of the DSA include:
- Requirements for online platforms to remove counterfeit listings swiftly.
- Increased liability for platforms failing to prevent counterfeit sales.
- Stricter transparency requirements for third-party sellers.
5. How Do Trade Agreements Influence Anti-Counterfeiting Measures?
International trade agreements often contain provisions on intellectual property rights and counterfeiting. Agreements such as the USMCA and the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) emphasize the importance of anti-counterfeiting efforts among signatory nations.
Important trade agreements impacting counterfeiting:
- USMCA: Strengthens trademark and copyright protections in North America.
- CPTPP: Enforces IP protections and encourages cooperation against counterfeiting among 11 countries.
6. What Role Do Customs Regulations Play in Counterfeiting Prevention?
Customs regulations are instrumental in detecting counterfeit goods at borders. Many countries employ advanced technologies and partnerships to prevent the import and export of counterfeit products, aiding enforcement of intellectual property laws.
Examples of customs regulations include:
- Automated Cargo Scanning: Customs agencies use X-ray machines and AI tools to detect counterfeit goods.
- Increased Penalties: Some regions enforce higher penalties for companies importing counterfeit goods.
7. What Are the Penalties for Counterfeiting in Major Markets?
Penalties for counterfeiting vary greatly depending on the region and the severity of the offense. In markets with strong intellectual property laws, such as the U.S. and Europe, fines and criminal charges can be substantial.
Typical penalties include:
- Fines: Up to $2 million for severe cases in the U.S.
- Imprisonment: Offenders may face jail time for large-scale counterfeiting.
- Asset Forfeiture: Seized goods and profits may be forfeited as part of the penalty.
8. How Does the Counterfeit Goods Seizure Process Work?
When customs officers identify counterfeit goods, they follow a seizure process that includes notifying the trademark owner and potentially initiating a legal process. This section explains the typical steps taken during a counterfeit seizure.
Steps in the seizure process:
- Identification by customs officers.
- Notification of the brand or trademark owner.
- Legal proceedings if necessary.
9. How Are Consumers Protected from Counterfeit Goods Online?
Legislative changes now place more responsibility on e-commerce platforms to protect consumers from counterfeit goods. Measures include stricter verification of sellers and penalties for platforms that allow counterfeit sales.
Consumer protections include:
- Transparent seller verification processes.
- Automated counterfeit detection tools on e-commerce sites.
10. How Are Small Businesses Affected by Anti-Counterfeiting Legislation?
Anti-counterfeiting laws aim to protect both large and small businesses from losing revenue to counterfeiters. While these laws support small businesses, compliance can sometimes impose costs, especially for companies in highly regulated industries.

Ways legislation impacts small businesses:
- Improved market fairness due to reduced competition from counterfeiters.
- Potential financial and time investment in compliance.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Key Legislation | TRIPS, EUIPO, Lanham Act |
| Technologies | Blockchain, AI, RFID |
| Customs | Automated Scanning, Penalties |
| Consumer Protection | Online verification, Seizure processes |
FAQs on Legislative Changes in Counterfeiting Prevention
1. What is the main international agreement for anti-counterfeiting?
The TRIPS Agreement under the WTO sets international standards for anti-counterfeiting measures.
2. How does the EU Digital Services Act help prevent counterfeiting?
The DSA requires online platforms to prevent and remove counterfeit goods actively.
3. What technology aids counterfeiting prevention?
Technologies such as blockchain, RFID, and AI improve product authentication and tracking.
4. How are consumers protected on online marketplaces?
Platforms are legally obliged to verify sellers and remove counterfeit products.
5. What are the penalties for counterfeiting in the U.S.?
Penalties include fines, imprisonment, and asset forfeiture.
6. Are customs regulations critical to counterfeiting prevention?
Yes, customs are a frontline defense, inspecting goods and seizing counterfeits at borders.
7. How does anti-counterfeiting legislation affect small businesses?
Legislation benefits small businesses by leveling the market but may also require compliance costs.


