What Makes Messaging Ambiguous?
1. What is Ambiguity in Messaging?
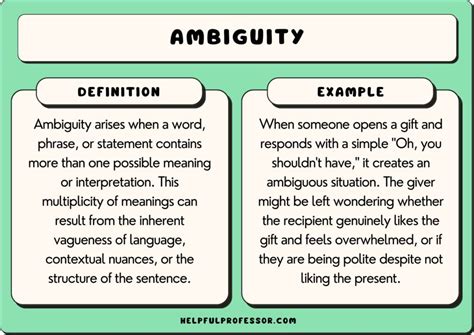
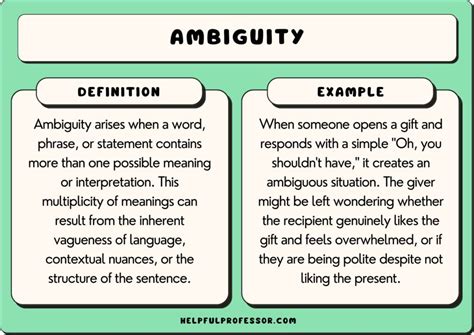
Ambiguity in messaging refers to the lack of clarity or multiple interpretations that can arise when a message is not explicit. This occurs when words, phrases, or sentences are structured in a way that makes them open to more than one meaning. Whether intentional or unintentional, ambiguity in communication can lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and confusion.
In some cases, ambiguity might be used purposefully, such as in literature or advertising, to engage the audience. However, in most everyday communications, ambiguity is often problematic because it hinders clear and effective communication.
Some common causes of ambiguity in messaging include:
- Vague or imprecise language
- Contextual differences
- Ambiguous grammar or sentence structure
- Inadequate information or missing details
Consider the sentence: “The chicken is ready to eat.” Is the chicken ready to be eaten, or is the chicken itself about to eat? This simple example demonstrates how unclear language can lead to multiple interpretations.
The key challenge with ambiguous messaging is that it can disrupt the intended message and create unnecessary confusion among the audience.
2. What are the Common Types of Ambiguity in Messaging?
There are different types of ambiguity that can affect the clarity of a message. Understanding these categories helps in identifying and reducing ambiguity in communication.
Lexical Ambiguity
This type occurs when a word has more than one meaning. For example, the word “bank” could refer to a financial institution or the side of a river.
Syntactic Ambiguity
Syntactic ambiguity arises from sentence structure or grammar. A sentence like “Visiting relatives can be boring” can either mean that the act of visiting relatives is boring, or that the relatives who are visiting are boring.
Semantic Ambiguity
This form of ambiguity happens when the meaning of a sentence as a whole is unclear. For example, “He saw her duck” could mean he observed a bird, or that he witnessed someone avoiding something by bending down.
Pragmatic Ambiguity
Pragmatic ambiguity is dependent on context. For instance, “Are you going to the party?” could be a casual question or a rhetorical statement, depending on the situation.
Scope Ambiguity
When quantifiers or logical operators are involved, scope ambiguity can arise. For example, “All students didn’t attend the lecture” can mean either no students attended, or not all students attended.
Being mindful of these types can help communicators craft clearer messages.
3. How Does Ambiguous Messaging Affect Communication?
Ambiguity in messaging can severely impact communication by introducing misunderstandings and confusion. In professional and personal settings, ambiguous messages can create frustration, tension, and errors in decision-making.
The effects of ambiguous messaging include:
- **Misinterpretation:** The receiver may understand a completely different message than intended.
- **Delay in response:** The need for clarification may delay actions or decisions.
- **Loss of credibility:** Frequent use of ambiguous language can erode trust and professionalism.
- **Conflict:** Differing interpretations of a message may lead to disagreements or conflicts.

For example, if a manager sends an email saying, “Let’s finalize the report soon,” without specifying a clear deadline, the team might interpret “soon” differently, leading to delays or incomplete work. In such cases, clarity is key to ensuring that all parties involved share the same understanding.
4. How Can Ambiguity Be Reduced in Communication?
Reducing ambiguity is essential for clear and effective communication. There are several strategies that communicators can employ to minimize ambiguity and improve the clarity of their messages.
1. Be Specific
Avoid vague language by providing specific details. Instead of saying “soon,” give an exact date or time.
2. Use Clear Pronouns
When using pronouns like “he,” “she,” or “it,” make sure it’s clear who or what you’re referring to. In complex sentences, use proper nouns when necessary.
3. Check for Multiple Meanings
Before sending a message, review the words you’ve used to ensure they don’t have multiple interpretations, particularly in different contexts.
4. Use Active Voice
Active voice tends to be clearer than passive voice. For example, “The manager approved the budget” is clearer than “The budget was approved.”
5. Provide Context
Including context helps the receiver understand the full scope of the message. Background information can reduce the chances of misinterpretation.
Employing these techniques can drastically reduce the chances of ambiguous messaging, helping ensure that your communication is clear, concise, and effective.
5. What Role Does Culture Play in Ambiguous Messaging?
Culture plays a significant role in how messages are interpreted, and what may be clear in one culture could be ambiguous in another. Different cultural backgrounds often have distinct communication styles, norms, and expectations.
In high-context cultures, like Japan or China, much of the communication relies on non-verbal cues, implied meanings, and context. On the other hand, in low-context cultures like the United States or Germany, communication tends to be more direct and explicit.
When communicating across cultures, ambiguity can arise if the sender’s intended message is understood differently based on the receiver’s cultural context. For example, a statement like, “We’ll think about it,” may be interpreted as a polite rejection in some cultures, while in others, it may indicate that further consideration is genuinely needed.
To reduce ambiguity in cross-cultural communication:
- Be aware of cultural differences in communication styles.
- Ask clarifying questions when unsure of meaning.
- Use more explicit language when communicating with people from different cultures.

6. How Does Ambiguity in Messaging Impact Business Communication?
In business, ambiguity can lead to significant consequences, such as project delays, poor decision-making, and misalignment between teams or stakeholders. When business communication is unclear, it can negatively affect productivity and outcomes.
Some specific impacts of ambiguity in business communication include:
- **Missed deadlines:** Vague instructions may lead to misunderstandings about timelines.
- **Inaccurate reports:** Ambiguous data or information can lead to incorrect conclusions and actions.
- **Unclear roles:** If responsibilities are not clearly defined, team members may not know what is expected of them.
- **Damaged relationships:** Miscommunication can erode trust between clients, customers, and colleagues.
For businesses, it’s essential to prioritize clear and concise communication to ensure that all team members, clients, and stakeholders have the same understanding of goals and expectations.
7. Can Ambiguous Messaging Be Beneficial in Any Way?
While ambiguity is often seen as a communication flaw, it can sometimes be beneficial. In certain scenarios, ambiguity allows for creative interpretation or helps soften the delivery of sensitive messages.
Some potential benefits of ambiguous messaging include:
- **Encouraging creativity:** Ambiguity in advertising or storytelling can encourage the audience to think critically and interpret the message in a way that resonates with them personally.
- **Diplomatic communication:** In diplomacy or negotiation, ambiguous language can help maintain flexibility and avoid offending parties.
- **Stimulating curiosity:** Ambiguity can create intrigue and keep audiences engaged, as they seek to uncover the full meaning of a message.
For example, a slogan like “Just Do It” is somewhat ambiguous, leaving the interpretation open to the audience. This allows the message to resonate with a broad range of people and situations, enhancing its impact.
8. How Does Technology Contribute to Ambiguous Messaging?
Technology, particularly in digital communication, can contribute to ambiguity in messaging. Text-based communication, such as emails, texts, or social media posts, lacks non-verbal cues like tone of voice, facial expressions, and gestures, which can lead to misunderstandings.
Some common technological factors that contribute to ambiguity include:
- **Autocorrect errors:** Automated tools may change words, leading to unintended meanings.
- **Character limits:** Platforms like Twitter have character limits, forcing users to condense their messages, sometimes at the cost of clarity.
- **Emojis:** While emojis can add context to digital communication, they can also be interpreted differently depending on the receiver’s perspective.
To reduce ambiguity in digital communication, it’s important to be mindful of these factors and take extra care to clarify meaning where necessary.
9. How Do Personal Biases Influence Ambiguity in Messaging?
Personal biases can shape how messages are interpreted, potentially introducing ambiguity. Our past experiences, beliefs, and assumptions influence how we understand language, and these biases may cause us to misinterpret messages.
Some ways in which biases contribute to ambiguity include:
- **Confirmation bias:** We tend to interpret messages in a way that aligns with our pre-existing beliefs.
- **Cultural bias:** Our cultural background shapes how we understand and interpret messages.
- **Emotional bias:** Emotions can influence our understanding of a message, especially if we are in a heightened emotional state.
Recognizing our own biases and seeking clarification when needed can help reduce ambiguity and improve communication.
10. How Can Feedback Help in Clarifying Ambiguous Messaging?
Feedback plays a crucial role in reducing ambiguity and ensuring that messages are understood as intended. Encouraging open feedback allows the sender to clarify any points of confusion and the receiver to ask for further details when necessary.
Strategies for using feedback to clarify ambiguous messaging include:
- **Ask open-ended questions:** This encourages the receiver to elaborate on their understanding of the message.
- **Paraphrasing:** Ask the receiver to paraphrase the message in their own words to confirm understanding.
- **Provide examples:** When giving feedback, use specific examples to illustrate points that may need clarification.
By incorporating feedback into the communication process, both parties can ensure that the message is clear and understood correctly.
Summary Table
| Question | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What is Ambiguity in Messaging? | Lack of clarity, multiple interpretations, leads to confusion |
| What are the Common Types of Ambiguity? | Lexical, syntactic, semantic, pragmatic, scope ambiguity |
| How Does Ambiguity Affect Communication? | Misinterpretation, delays, conflict, loss of credibility |
| How Can Ambiguity Be Reduced? | Be specific, use clear pronouns, provide context, active voice |
| What Role Does Culture Play? | Different communication styles, cultural norms impact interpretation |
| How Does Ambiguity Impact Business Communication? | Delays, misalignment, damaged relationships, missed deadlines |
| Can Ambiguity Be Beneficial? | Creativity, diplomatic communication, stimulating curiosity |
| How Does Technology Contribute? | Lack of non-verbal cues, autocorrect, emojis, character limits |
| How Do Personal Biases Influence Ambiguity? | Confirmation bias, cultural bias, emotional bias |
| How Can Feedback Clarify Ambiguity? | Open-ended questions, paraphrasing, examples |