Understanding Regulatory Bodies that Certify Products: A Complete Guide
1. What Are Regulatory Bodies and Why Are They Important?
Regulatory bodies are organizations responsible for establishing standards, enforcing regulations, and certifying products to ensure they meet required safety, quality, and environmental standards. Certification is essential for public safety, quality assurance, and legal compliance, which is particularly important in industries such as food, health, construction, and electronics.
These bodies often work under government oversight or operate as third-party entities with accreditation. They establish protocols for product testing, assessment, and compliance to assure consumers and stakeholders. Below is a breakdown of why these regulatory entities matter:
- Public Safety: Ensures that products meet health and safety standards.
- Quality Assurance: Provides consistency and reliability across products.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces negative effects on the environment through adherence to green standards.
- Market Access: Allows certified products to access broader, regulated markets.
Companies must meet these requirements to obtain certifications, ensuring their products are safe, reliable, and in alignment with legal guidelines. Different industries may rely on different types of regulatory bodies for certifications, each with specific mandates and criteria.
2. What Types of Products Require Certification by Regulatory Bodies?
Various product categories require certification from regulatory bodies to verify safety, quality, and adherence to industry standards. The scope of certified products spans multiple sectors including food, construction materials, medical devices, consumer electronics, and more. Here’s a breakdown of major product categories and typical regulatory requirements:
| Product Category | Certification Requirements | Regulatory Bodies |
|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverages | Hygiene, safety, labeling | FDA, USDA, HACCP |
| Consumer Electronics | EMI/EMC, safety standards | FCC, UL |
| Medical Devices | Safety, efficacy, labeling | FDA, CE Marking |
| Construction Materials | Strength, durability, safety | ASTM, ISO |
Each regulatory body has specific requirements tailored to industry needs and local laws, meaning companies must align their products to these specifications to access various markets. Certification not only ensures compliance but also provides credibility and trustworthiness among consumers and stakeholders.
3. How Do Regulatory Bodies Test Products for Certification?
The testing process for product certification involves rigorous checks and evaluations performed by regulatory bodies. Here’s a detailed look at the certification process:
- Application and Documentation Review: Companies submit an application with detailed documentation regarding product specifications, materials used, and intended usage.
- Sample Selection and Testing: Regulatory bodies obtain product samples and perform laboratory tests to assess compliance with standards.
- Compliance Verification: Testing evaluates various criteria such as durability, safety, environmental impact, and performance.
- Issuance of Certification: If a product meets all requirements, it is granted certification, allowing it to be sold in specific markets.
The entire process varies depending on the regulatory body and product category but remains a cornerstone for ensuring products meet essential quality and safety requirements.
4. What Are Some Major Regulatory Bodies for Food and Beverage Products?
Food and beverage products must meet stringent safety, quality, and hygiene standards, which are monitored and enforced by major regulatory bodies worldwide. These organizations establish rules regarding ingredients, labeling, processing, and storage. Here are some prominent regulatory bodies in the food industry:
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration): Oversees food safety in the United States, setting standards for safe consumption, labeling, and additives.
- USDA (U.S. Department of Agriculture): Focuses on meat, poultry, and egg products, ensuring they are safe and accurately labeled.
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority): Regulates food standards across Europe, providing scientific advice on food-related risks.
- HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points): An internationally recognized system focusing on food safety management and contamination prevention.
Food certification helps prevent health hazards and ensures that products are safe for consumption. This, in turn, builds consumer trust and supports global food trade by aligning standards internationally.
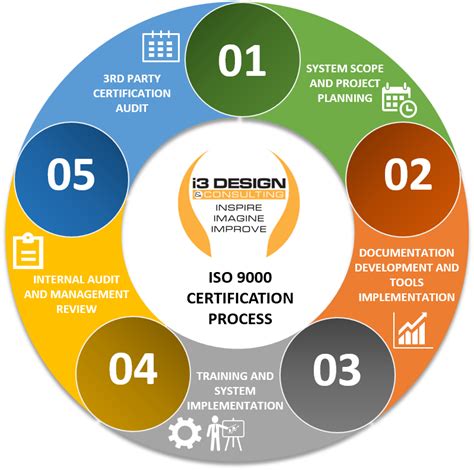
5. How Can Companies Achieve ISO Certification?
ISO certification is a mark of quality and process adherence that is recognized globally. To achieve ISO certification, a company must meet the standards set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which ensures operational efficiency, quality management, and environmental responsibility. The steps to ISO certification include:
- Determine relevant ISO standards (e.g., ISO 9001 for quality, ISO 14001 for environmental management).
- Implement necessary processes and document procedures according to ISO requirements.
- Conduct an internal audit to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Hire an accredited external auditor to review and verify adherence to ISO standards.
- Upon successful audit, receive ISO certification, which must be maintained with periodic audits.