The Effects of Counterfeiting: A Comprehensive Analysis
1. What are the economic impacts of counterfeiting?
Counterfeiting significantly affects economies worldwide. It leads to lost revenues for legitimate businesses, job losses, and reduced tax income for governments. Estimates suggest that counterfeiting costs the global economy over $500 billion annually.
One of the primary economic impacts is the diversion of sales from genuine products to counterfeit ones. This shift can lead to:
- Reduced profitability for manufacturers.
- Increased costs for law enforcement and legal systems.
- Job losses in sectors heavily affected by counterfeiting.
Additionally, counterfeiting undermines brand reputation. Companies invest heavily in marketing and quality control, and counterfeit products can damage consumer trust. This leads to long-term repercussions for brand loyalty and market position.
Counterfeit goods also result in lower quality products entering the market, which can affect consumer safety. For example, counterfeit pharmaceuticals can have severe health implications.
Table: Economic Impacts of Counterfeiting
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Lost Revenue | Estimated at over $500 billion globally. |
| Job Losses | Reduction in employment opportunities in affected sectors. |
| Brand Damage | Long-term harm to company reputation and consumer trust. |
| Legal Costs | Increased expenditure on enforcement and legal actions. |

2. How does counterfeiting affect consumer safety?
Counterfeiting poses significant risks to consumer safety, particularly in industries such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, and automotive parts. Counterfeit products often lack the rigorous testing and quality assurance that legitimate products undergo.
For example, counterfeit medications may contain incorrect dosages or harmful substances, leading to serious health risks. Similarly, counterfeit automotive parts can compromise vehicle safety, increasing the likelihood of accidents.
Table: Risks Associated with Counterfeit Products
| Product Type | Potential Risk |
|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Health complications due to incorrect formulations. |
| Electronics | Fire hazards and device malfunction. |
| Automotive Parts | Increased accident risks due to failure. |

3. What are the legal implications of counterfeiting?
Counterfeiting is a criminal offense in most jurisdictions, carrying severe penalties. Legal implications extend beyond the counterfeiters to businesses and consumers affected by the crime.
Companies that produce counterfeit goods can face hefty fines, imprisonment, and civil lawsuits from trademark holders. Additionally, legitimate businesses may invest in costly legal battles to protect their intellectual property.
Table: Legal Penalties for Counterfeiting
| Type of Violation | Possible Penalties |
|---|---|
| Trademark Infringement | Fines and imprisonment. |
| Copyright Violation | Injunctions and damages awarded. |
| Fraud | Criminal charges and restitution. |

4. How do consumers perceive counterfeit products?
Consumer perception of counterfeit products varies widely. Some consumers knowingly purchase counterfeit items for their lower prices, while others may not realize they are buying fakes.
Studies indicate that price sensitivity often drives the decision to purchase counterfeits. However, many consumers express concern over the quality and safety of counterfeit products.
Table: Consumer Perception Factors
| Factor | Impact on Purchase Decision |
|---|---|
| Price | Lower prices can attract buyers. |
| Brand Trust | Decreased trust in brands affected by counterfeiting. |
| Quality | Concerns over safety and performance. |
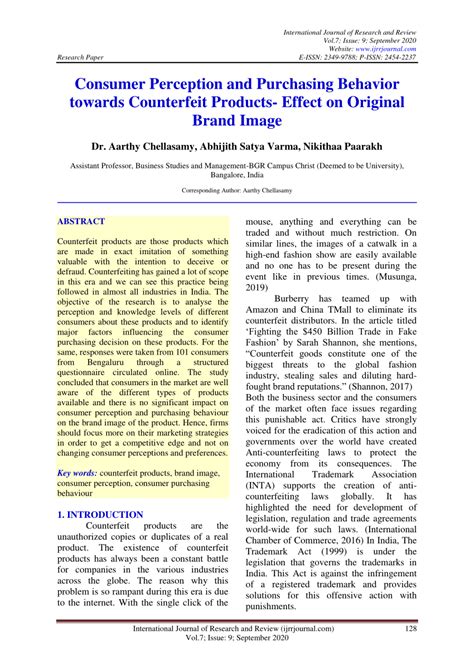
5. What industries are most affected by counterfeiting?
Counterfeiting impacts a wide range of industries, but some sectors are more vulnerable than others. The fashion, technology, and pharmaceutical industries consistently face significant threats from counterfeit goods.
The fashion industry suffers from fake designer items, which can undermine brand integrity. Similarly, technology companies are frequently targeted by counterfeit electronics, which can pose safety risks to consumers.
Table: Industries Affected by Counterfeiting
| Industry | Type of Counterfeit Products |
|---|---|
| Fashion | Fake designer apparel and accessories. |
| Technology | Counterfeit smartphones and components. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Fake medications and health products. |
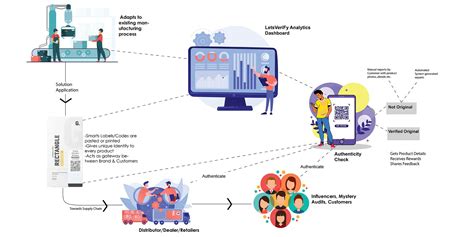
6. What role does technology play in combating counterfeiting?
Technology plays a crucial role in the fight against counterfeiting. Innovations such as blockchain, RFID tags, and holograms are being used to verify product authenticity and enhance traceability.
Blockchain technology, for instance, provides a decentralized ledger that can record every transaction related to a product, ensuring transparency throughout the supply chain.
Table: Technologies to Combat Counterfeiting
| Technology | Use |
|---|---|
| Blockchain | Transparency and traceability in supply chains. |
| RFID Tags | Real-time tracking of products. |
| Holograms | Visible authentication features on products. |
7. How do international trade agreements address counterfeiting?
International trade agreements often include provisions to combat counterfeiting. These agreements seek to harmonize laws and enhance cooperation among countries in enforcing intellectual property rights.
For example, the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) sets minimum standards for IP protection and enforcement, which member countries must adhere to.
Table: Key International Agreements Against Counterfeiting
| Agreement | Focus |
|---|---|
| TRIPS | Minimum IP protection standards. |
| ACTA | Enforcement of intellectual property rights. |
| TPP | Comprehensive trade and IP provisions. |

8. What can businesses do to protect themselves from counterfeiting?
Businesses can adopt several strategies to protect themselves from counterfeiting. These include strengthening brand identity, investing in anti-counterfeit technologies, and educating consumers.
Developing a strong brand presence helps consumers recognize legitimate products. Additionally, implementing technologies like RFID and blockchain can enhance product traceability.
Table: Strategies for Businesses
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Brand Strengthening | Building a recognizable and trustworthy brand. |
| Anti-Counterfeit Technology | Investing in innovative verification solutions. |
| Consumer Education | Informing customers about genuine products. |

9. How does counterfeiting affect global supply chains?
Counterfeiting disrupts global supply chains by introducing fake products into the market. This can lead to inefficiencies, increased costs, and loss of consumer confidence.
For instance, counterfeit components can cause production delays and product recalls, significantly impacting a company’s bottom line.
Table: Effects of Counterfeiting on Supply Chains
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Production Delays | Counterfeit parts can halt manufacturing processes. |
| Increased Costs | Costs associated with legal actions and recalls. |
| Consumer Distrust | Decreased trust in brands and products. |

10. What are the future trends in combating counterfeiting?
As counterfeiting becomes more sophisticated, future trends in combating it will focus on technology and international collaboration. Enhanced data analytics, AI, and machine learning will play crucial roles in identifying and preventing counterfeiting activities.
Moreover, greater international cooperation is essential to effectively tackle the global nature of counterfeiting. Collaborative efforts can help streamline enforcement processes and share best practices among nations.
Table: Future Trends in Anti-Counterfeiting
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Analytics | Using data to identify counterfeit patterns. |
| AI and Machine Learning | Automating detection of counterfeit products. |
| International Cooperation | Collaborative efforts to enhance enforcement. |

Summary Table
| Question | Key Insights |
|---|---|
| Economic Impacts | Counterfeiting costs the global economy over $500 billion. |
| Consumer Safety | Risks from counterfeit medications and parts. |
| Legal Implications | Severe penalties for counterfeiting offenders. |
| Consumer Perception | Varied perceptions influenced by price and quality. |
| Affected Industries | Fashion, technology, and pharmaceuticals are heavily impacted. |
| Technology’s Role | Innovative solutions like blockchain enhance authenticity. |
| International Agreements | Provisions in agreements like TRIPS help combat counterfeiting. |
| Business Protection | Strategies include brand strengthening and technology investment. |
| Supply Chain Effects | Counterfeiting leads to inefficiencies and consumer distrust. |
| Future Trends | Focus on AI and international collaboration in countering counterfeiting. |
FAQ
1. What is counterfeiting?
Counterfeiting is the act of producing fake goods that imitate genuine products to deceive consumers.
2. Why do people buy counterfeit products?
Many consumers buy counterfeit products due to lower prices, often unaware of the potential risks involved.
3. What can be done to prevent counterfeiting?
Preventive measures include technological innovations, consumer education, and stricter law enforcement.
4. Are counterfeit products always of poor quality?
Not always; some counterfeit products can appear to be of high quality, making them difficult to detect.
5. How does counterfeiting affect small businesses?
Small businesses can suffer significant financial losses and damage to their reputation due to counterfeiting.
6. Can consumers report counterfeiting?
Yes, consumers can report counterfeit products to local authorities or brand owners.
7. What is the role of consumers in combating counterfeiting?
Consumers play a crucial role by being vigilant and educated about the products they purchase.


